Description and operation of the jaundice bulb
What is a lamp for jaundice
In 32-86% of newborns in the first week of life, mainly on the second-third day, there is the so-called physiological jaundice, manifested outwardly by jaundice of the skin and sclerae of the eyes.
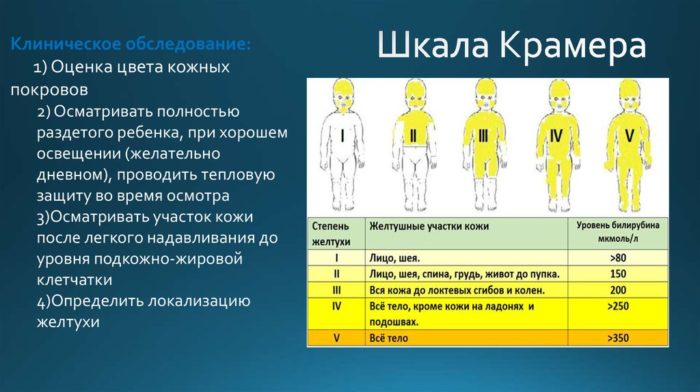
The phenomenon itself is not abnormal and occurs because of the reduced level of liver enzymes and, as a consequence, the insufficient rate of decomposition of indirect bilirubin in the liver, which is formed during the decomposition of dying red blood cells and hemoglobin. The most common causes are:
- Prematurity and/or low birth weight;
- Endocrine disorders in the mother, especially diabetes mellitus and thyroid disease;
- Rh blood conflict between mother and child;
- Hestosis during pregnancy.
It takes from one and a half to three months for the child's enzyme system to develop fully. In the initial period of formation, therapy is aimed at combating hyperbilirubinemia. It is indirect bilirubin that poses the greatest danger to the newborn because of its histotoxicity - its ability to adversely affect metabolic processes in tissues, including the brain.
There are 25 known forms of neonatal jaundice, and only the rarest of them require medical or surgical treatment. In 95% of cases, this condition is compensated by phototherapy lamps emitting a spectrum of light close to ultraviolet.
How it Works
Under the influence of lamps that emit light with a wavelength of 400-500 nm in the skin is photoisomerization of indirect bilirubin molecules with its transition into the water-soluble form. The resulting direct bilirubin is not dangerous and is easily excreted by the body's excretory systems with urine, feces, and to some extent with sweat.
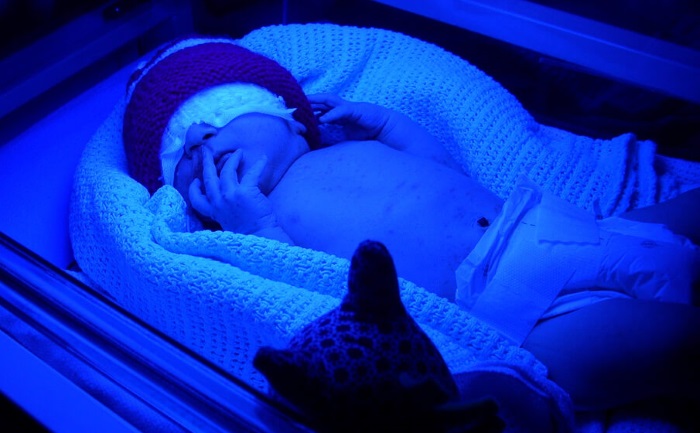
The therapeutic effect appears:
- laboratory - reduction of bilirubin level in blood already on the second day of phototherapy and complete normalization on the 5th-6th day;
- visually - reduction of jaundice of skin, mucous membranes and sclerae of eyes on the third-fourth day of treatment.
For note. Coloring of a newborn stool dark green during phototherapy is a normal phenomenon due to excretion of direct bilirubin and presents no danger. It can be taken into account as an additional indicator of the efficacy of the lamp treatment.
Experimentally it was determined that the greatest degree of photoisomerization is achieved by irradiation with light of the blue spectrum and a wavelength of 450-460 nm narrow range. The use of ultraviolet lamps Not as effective for infants, because their operating range is between 100 and 400 nanometers, which is dangerous for the immature body of infants.
Variety
Depending on the design there are lamps:
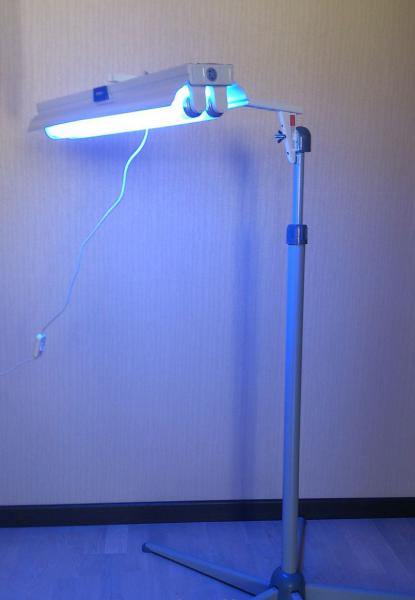
- overhead lights - mounted on a portable tripod or in a fixed panel connected to a cuvette. The main disadvantage is the requirement to protect the genitals and the organs of vision in the case of light sources close to the aggressive ultraviolet range;

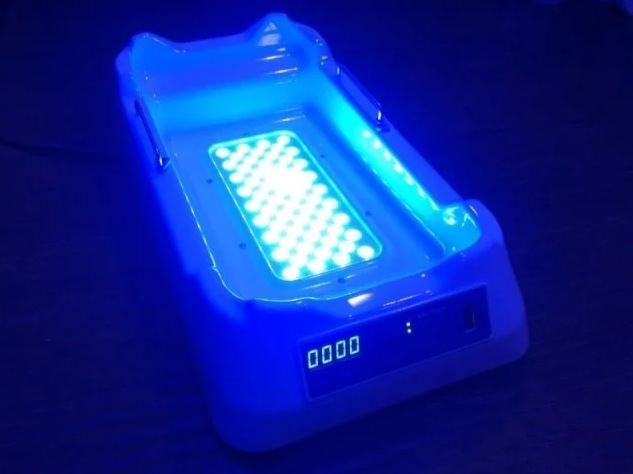
- lower light - lamps located at the bottom of a cuvette with a transparent bottom, or under a hammock with a translucent cloth. Less demanding to protect the eyes, as long as the child's posture is observed or safe LED lights are used;

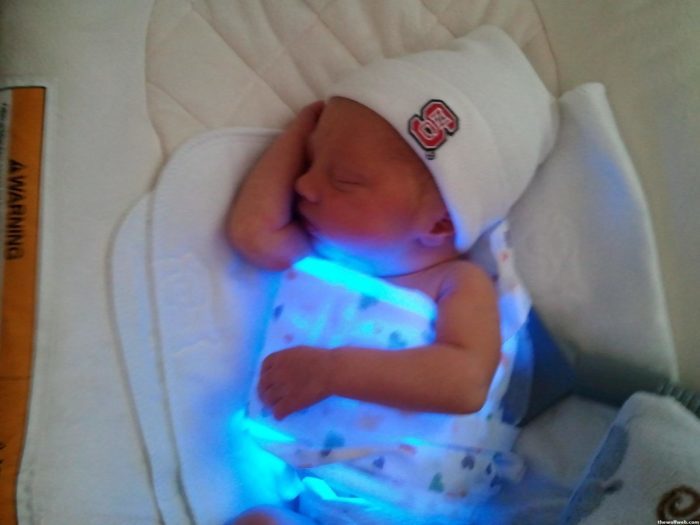
- wrap-around fabric with a fiber optic cable located on the inside surface of the blanket or bedspread. The development of American scientists is considered safe and convenient, as the light rays are directed inside and do not get into the eyes, and the small volume of the blanket when folded allows you to carry it with you and use it wherever there is a power source.

As an alternative to lamps in countries with warm climates, sunlight passed through a special filtering fabric is used. This material cuts off the ultraviolet and infrared range, letting in only the blue spectrum of visible light. The child is placed under the canopy of filtering fabric, and is undressed under it throughout the day. Studies have shown that the therapeutic effect of filtered sunlight is not inferior, and in some groups even exceeds that of phototherapy with electric lamps. The only disadvantage of the method is the need to monitor the infant's temperature, and if the body temperature reaches 38 °C, place it in the shade until the thermometer readings normalize.
Design differences of photo-lamps from jaundice for the comfort of the newborn and the result of treatment are not of fundamental importance, since different types of lighting elements can be used in the same units. Some types of lamps have a limited useful life. This means that an outwardly working device's efficiency decreases over time. Newer units are equipped with special meters that mark the "mileage" of the lamp. The status and efficiency of a lamp without a meter is determined by a photometer.
Jaundice in newborns: causes, treatment needed
LED or LED devices
The most economical and safe sources of light. It is LEDs are mounted in cuvettes with a transparent bottom. Since these lamps are practically not heated, they can be placed at any convenient distance from the body of the baby, and the intensity of the blue spectrum with a wavelength of 420-470 nm power of 500 microW/cm2 at a distance of 800 mm from the body eliminates the harmful effects of high- and low-wave radiation. The peculiarity of LED devices is that their light is less effective, but relatively safe for the visual organs and skin of the newborn. Another positive difference of LEDs is their lifespan, which is 20,000-50,000 hours of operation. LED lamps are a full-fledged replacement for halogen and fluorescent devices.
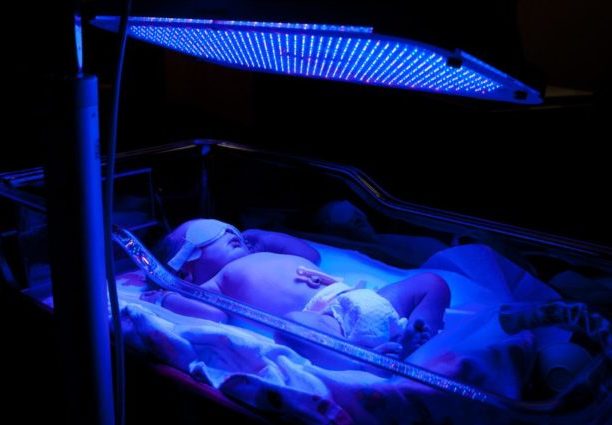
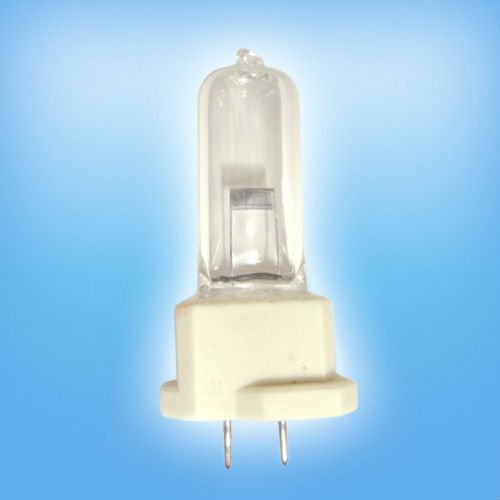
Halogen lamps
Improved incandescent lamps with a tungsten filament housed in a bulb with iodine or bromine vapor. Filters are used to cut off unnecessary radiation waves, but halogen lamps operate in the 380-600 nm range and their light output reaches 22 Lm/W, which makes special efforts to protect the eyes and groin from light burns. In addition, the temperature of the bulb heating at 300 °C implies placing the device at a distance from the patient to avoid hyperthermia, which reduces the concentration of the light flux. Halogen units have a maximum operating time of 4000 hours. Uneven distribution of the useful spectrum and increased requirements for control of possible hyperthermia and overdose of UV radiation make the use of halogen lamps in devices for the treatment of hyperbilirubinemia unreasonable.

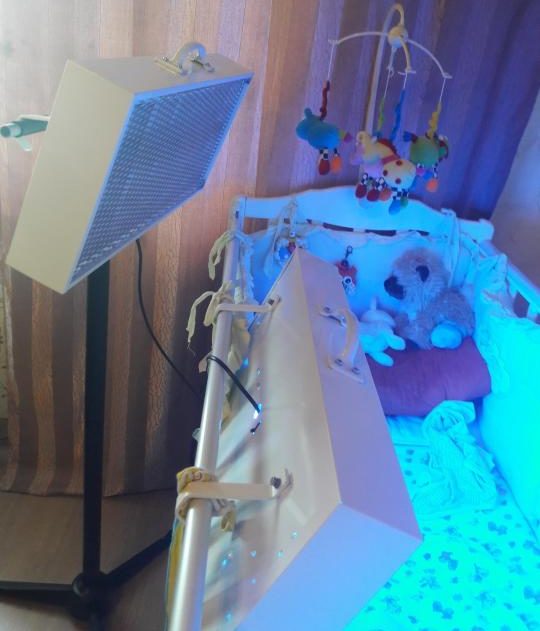
Fluorescent photo lamps.
They are most commonly used as bactericidalBecause the electrical discharge in the mercury vapor is capable of producing a wide range of light waves, from the green visible spectrum of 520 nm all the way up to the aggressive low-wave class B ultraviolet. For the treatment of jaundice, gas-discharge devices with turquoise light at 490 nm and blue light at 420-460 nm are suitable. In terms of power consumption they are not inferior to LEDs with the same power of the light flux, and the working life is up to 70 thousand hours. Low heat dissipation does not lead to hyperthermia and allows the installation of fluorescent bulbs in devices without special heat sinks and forced cooling. Some disadvantages:
- presence of poisonous mercury inside the fragile bulb;
- Frequent breakdown of triggering devices;
- burnout of light-forming photocells and photofilters in the bulb with a change in the operating range in the ultraviolet direction.
All this requires attention to operating conditions, maintenance and protection of the child's eyes and groin area from burns. In this, fluorescent lamps are inferior to LED lamps.

Hybrid
A combination of overhead and underhead lamps, where LEDs are installed in the bottom of the cuvette and halogen or fluorescent lamps. In some cases, combinations of bottom light and photo-optical covers are used. Combined systems are used when it is necessary to achieve maximum effect in a short period, but the application requires special skills of the operating staff.

How to choose the right lamp
Inpatient neonatal centers allow the use of all types of devices and their combinations, as all indicators and the baby's condition are monitored by professional doctors. In cases where the attending physician allows phototherapy at home, the conditions for choosing a device for the treatment of neonatal jaundice are:
- Safety.
- Mobility.
- Ease of use.
Two types of lamps fit these criteria:
- Portable cuvettes with a lower light or tripods on LED elements. They do not damage eyesight, practically do not lead to overdose of UV, hyperthermia. As a rule, they are equipped with electronic control system with a programmable operating mode and a counter showing the remaining useful life. At the same time they are relatively available and economical;
- Photoblankets and photocovers. They have all the advantages of LED lamps, but do not disturb the newborn, folded up into a small case. The main and only disadvantage is the high price and small range on the medical equipment market.
With a short course of treatment it is inexpedient to buy such equipment, so most parents are limited to the services of companies that provide the device for rent.
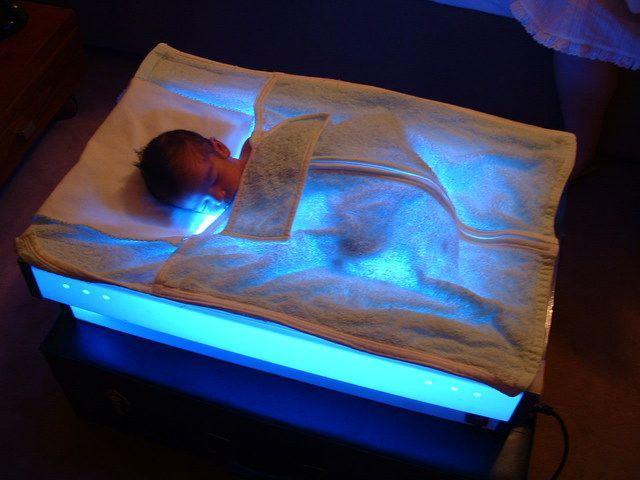
Indications and contraindications for use
The final decision on the advisability of using the conservative method of treatment of neonatal jaundice is made by the neonatologist or district pediatrician. Appointment of phototherapy is possible on the basis of examination, laboratory examination and maternal history, including during pregnancy. Most often light therapy is indicated in the following cases:
- Physiological jaundice of newborns with indirect bilirubin levels above 70 μmol/l in preterm infants, 60 μmol/l in premature infants.
- mild hemolytic disease of newborns, when the level of indirect bilirubin in blood serum does not exceed 60 μmol/l;
- maternal history of diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, severe gestosis, anemia during pregnancy;
- physiological immaturity of the premature newborn;
- preparation or rehabilitation before/after surgical interventions;
- Subcutaneous and parenchymatous hemorrhages in a child.
Absolute contraindications for phototherapy include:
- cholestasis due to bile duct obstruction;
- Bronze baby syndrome" - increased photosensitivity of the skin, when phototherapy leads to a grayish-brown coloring of the skin, urine and discoloration of stool;
- Inflammatory processes in liver tissue;
- Critical bilirubin levels that are life-threatening for the child due to CNS damage:
- for preterm babies 342 μmol/l;
- for premature infants 270 µmol/l;
- for deeply premature infants from 170 µmol/l.
In the presence of contraindications and in cases of ineffectiveness of phototherapy, when there is no time for conservative therapy, medical treatment is used, and in some cases surgical intervention is indicated.
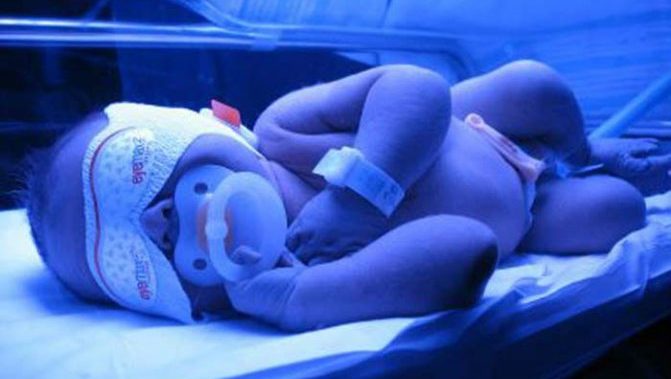
Instructions for use
Fluorescent lights.
- The newborn is removed from clothing, leaving a diaper, put on special protective goggles with a fixation under the chin to prevent involuntary slipping and placed in the cuvette.
- The device is turned on and set at a distance of 400-600 mm from the child's body.
- A timer is set from 30 minutes to 8 hours, depending on the neonatologist's instructions.
- The session is interrupted for feeding, diaper changes. The doctor should be notified if redness of the skin is detected and the baby becomes very anxious.
Halogen lamps
Because of the wide range of radiation that captures the ultraviolet range and the heating of the bulb up to 300 °C, halogen lamps are used with the utmost care in terms of safety, which includes:
- mandatory use of eye and genital area protection;
- positioning the lamp no closer than 800 mm to the child;
- monitoring the body temperature and identifying hyperemic areas of the skin.
For treatment with halogen devices, it is recommended that the child be hospitalized.
Combination systems
In the case of combinations of fluorescent and LED light sources, the treatment tactics correspond to the standard for a particular type of apparatus. If the combined system refers to therapy with a fiber-optic photo blanket, the technique of its application implies:
- exclusion of protective devices;
- daily cycle of therapy with breaks for hygienic procedures;
- the ability to feed without taking the newborn out of the photoblanket or blanket.

LED lights.
- The baby is undressed completely or down to the diaper. A cap or goggles are placed over the eyes to improve sleep quality.
- The patient is placed under the machine, in a cuvette or hammock face up.
- Using the control panel, the operating mode and session time specified by the treating pediatrician are set.
Duration of treatment
It is forbidden to independently determine the necessary course of treatment and duration of phototherapy periods. In home treatment, the district paediatrician is obliged to examine the patient and monitor the course of therapy throughout the course. Parents or babysitters follow all the doctor's instructions. In the normal course of phototherapy, the jaundice of the skin disappears completely on day 7-8. The manifestation of symptoms on the first day or persistent jaundice for more than 14 days is an abnormality and a reason to transfer the patient to the hospital for further examination and outpatient treatment.
Adverse reactions when using the lamps
Prolonged exposure to the blue light spectrum, even with full compliance with safety precautions, is sometimes accompanied by:
- Hyperemia of the skin, sometimes burns;
- Dryness and peeling of the epidermis;
- Hyperthermia;
- Disorders of the stool;
- Increased anxiety, sleep disorders.
In order to prevent water balance disorders, the child is given water or 0.9% NaCl with a spoon, and in severe cases, infusion therapy with 3% glucose solution is given.
How quickly bilirubin decreases
The final formation of the enzyme system of the liver of the newborn occurs by 1.5-3.5 months of life. Throughout the period, complications and relapses are possible. Treatment is considered effective if the indirect bilirubin level in the patient's blood drops by 19-21 µmol/day.