Features of the Wood lamp in dermatology
In 1903, scientist and inventor Robert Williams Wood created a filter that cut off all visible light except ultraviolet. The filter was a barium-sodium silicate glass with nickel or cobalt oxide added and was called a "Wood filter. Later the development found use in diagnostic medicine for the reason that under ultraviolet light lichen and other skin pathologies stand out with special colors and shades.
What is a Wood lamp
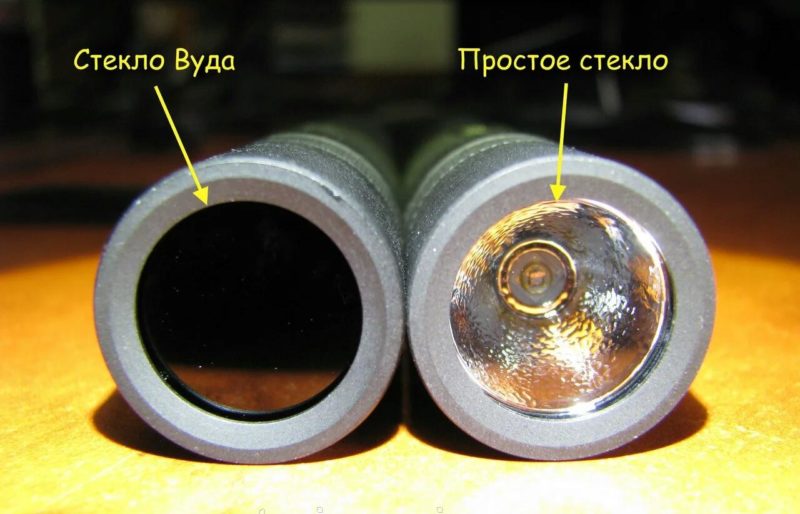
Actually, Robert Wood invented a kind of glass that transmits long-wavelength ultraviolet light in the range of 320-400 nm. Accordingly, his name became the name of the ultraviolet light source with a bulb of filtering material invented by the scientist. In addition, the device is sometimes called a "black lamp" because
- The glass has a dark blue, almost black color;
- The filter cuts off most of the light visible to the human eye, and when the device is on, objects with no luminescence effect appear black to humans.

From a technical point of view, neither the first nor the second option is correct, because the real black lamp is made of completely transparent glass and emits light in the 350-500 nm range. Such devices are used in traps for flying insects, as they are attracted to this range. The main property of the Wood lamp as a tool is the visualization of substances that can luminesce, that is, glow under the influence of ultraviolet light.
Varieties of
Now Wood's lamp is called any device that emits light in a narrow wavelength range of 320-400 nm, with filtering of the aggressive UVC, UVB and visible spectrum. There are devices designed according to three principles.
GRL
A low-pressure mercury discharge lamp with a range of 350-400 nm, with a filtered glass bulb. The device peaks at 365 nm.

Fluorescent
A fluorescent or halogen lamp. Placed in a transparent bulb with special types of phosphors sprayed on the inside that emit two wavelengths:
- 368-371 nm - with europium-activated strontium borate phosphor.
- 350-353 nm - with lead-activated barium silicate phosphor.

Ultraviolet
UV LEDs or LED cells made to emit a narrow range of soft luminescence at 365 nm.

Only the first option (wavelengths in the 320-400 nm range) fits the definition of Wood's classic invention, but the use of the original technology in the medical field has made the name justifiable for any light source with a range suitable for activating luminescence in the visible to the eye range.

Where to use
Depending on the spectrum of light emitted, the devices have found use in areas such as:
- Forensics - for illumination of biological traces of blood, sweat, fat, urine, semen, saliva;
- Medicine - for express diagnostics of dermatological diseases, laboratory research, hardening composite fillings;
- veterinary - most of the causative agents of skin diseases in humans and animals are the same;
- Radio engineering - for identification and classification of radio components;
- insecticide protection - in mosquito and mosquito traps;
- entertainment industry - in strobe lights, light shows, for identification of visitors to indoor events;
- trade and financial sphere - for illumination of banknotes, identification of barcodes, fixation of marked banknotes during investigations;
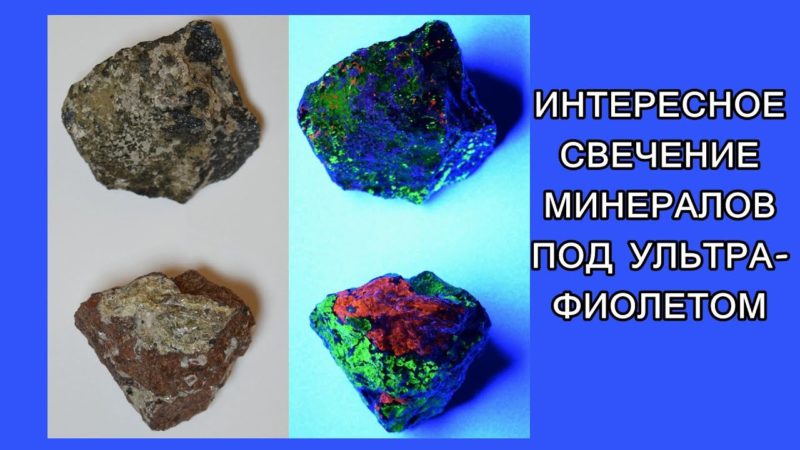
- Geology - to study minerals.

The main difference between the Wood lamp and UVL used for quartzing is the absence of aggressive radiation, as well as the glow visible to the human eye.
Using the lamp in dermatology
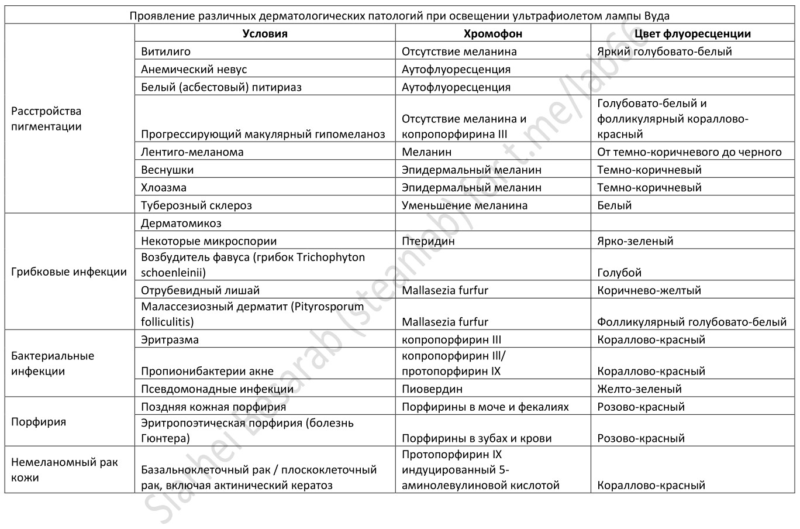
The Wood lamp was used in dermatology as early as 1925, when scientists Margaro and Davis discovered the phenomenon of fluorescence in the waste products of various microorganisms, especially fungi and bacteria. The lumdiagnostic method was based on the ability of pathogens to emit different colors.
How to conduct a skin examination
Preparation for the examination includes:
- Excluding the use of disinfectants and detergents, creams and ointments at least two days before the examination. Chemicals distort the color of the examined area of the body, and the destruction of traces of microorganisms reduces the intensity of their luminescence under UV rays.
- Cleaning of impurities on the eve of the examination - dirt and foreign substances are removed with clean running water. Drying is done with an electric dryer or with a dry (non-bactericidal) paper tissue using blotting motions.
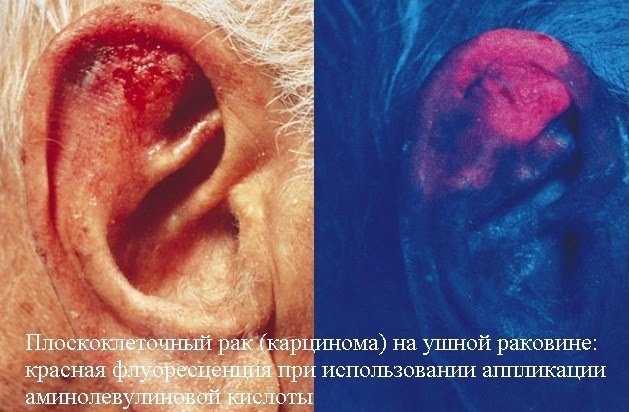
In some cases, such as when skin cancer is suspected, 4-5 hours before the examination, the dermatologist prescribes application of 20% aminolevulinic acid-based ointment on the examined body area to stimulate production of protoporphyrin IX fluorescent under UV rays - a diagnostic sign of carcinomas, Bowen disease, Paget's disease, solar keratomas.
Fluorescein solution or tetracycline paste is applied to the skin before lumodiagnosis to detect scabies mite passages.
The tactics of luminescent diagnostics are as follows:
- The device is turned on 5 minutes before the examination to bring the lamp to its optimal operating mode (not required for LED elements).
- The examination is performed in a darkened or completely dark room. The examiner must pre-adapt his or her vision to the darkness.
- The device is brought to the studied area of the body at a distance of 10-15 cm (5 cm is allowed for LED elements) from the skin surface.
Simplicity of the procedure makes it available for self-testing at home, all the more so because the instructions to the branded devices often have a comparative table with examples of the most common pathologies.
Self-diagnostics may be allowed only as a preliminary and serves as a reason to consult a specialist. Self-treatment on the basis of the examination is excluded.
Regular examinations of pets and farm animals are carried out on the same principle.
How shingles shines under the lamp
The most common diseases detected by the lumdiagnostic method:
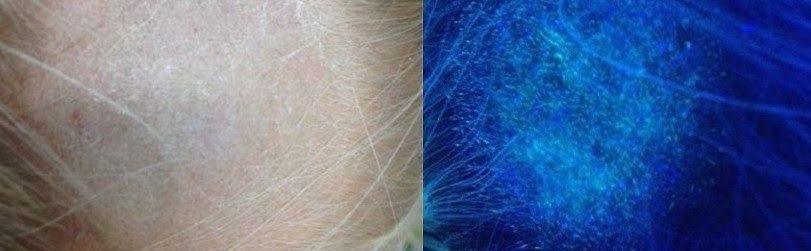
- Ringworm - shines under the Wood lamp with a bright green glow. However, note that some microsporia pathogens do not fluoresce;
- pseudomonad lichen - glows yellow-white or copper-colored;
- Pseudomonas infection - smears from the focus or purulent contents of wounds infected with Pseudomonas give a yellow-green glow under UVL;
- melasma - hyperpigmented spots and their boundaries under UVL contrast sharply with healthy skin.
The Wood invention is an initial non-invasive diagnostic tool, but the final diagnosis is made solely on the basis of a comprehensive examination, the tactics of which are determined by the treating physician.
How to make a lamp with your own hands
The technology of making a classic Wood lamp involves making a specific glass or sputtering a rare phosphor on the bulb. Much easier to buy any ultraviolet light source with the required range of waves within 320-400 nm and a standard socket format E27 or compact G23. If there is no letter L in the marking of the lamp, for example UV-9W-L, it means that it needs an original device to start it. To turn on such a lamp by screwing it into the socket of a table lamp will not work because there is no ECG - electronic control gear. To make it work you need to:
- Find any energy-saving fluorescent light bulb with a wattage identical to the ultraviolet bulb.
- Desolder the contacts from the filaments and disconnect the bulb.
- In the same way, unsolder the pins of the UV lamp and solder the ECG from the ELL to them. If the size of the contacts do not match, you need to connect the bulb to the board by means of wires.
- The resulting lamp mounted in any reflector from a street lamp or a table lamp of suitable dimensions.
Video: Making germicidal lamps from street lamps
When the outer phosphor bulb is destroyed, it exposes the inner bulb, which emits an aggressive spectrum below 300 nm. The device is not suitable for diagnostics due to the danger to humans.
Contraindications to use
Increased photosensitivity of the skin is the only contraindication to luminescent diagnostics. Specialist working with conditionally safe UV radiation must use special goggles for eye protection of O-45 UV "Vision" type or their analogues.
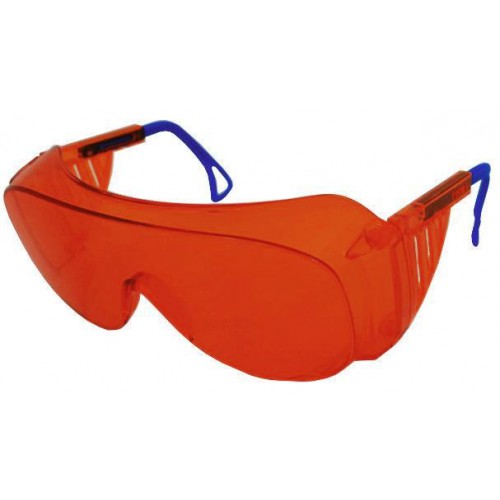

At home in case of short duration of exposure yellow polycarbonate glasses with light filter will do.