The basics of parallel and series connection of LEDs
LED technology - the latest advances in lighting technology, which has changed the lighting of homes, streets, public places, transportation. Their use has a number of features on the types of connection: series connection of LEDs, parallel or mixed. Each of these types has positive and negative sides. Serial allows connection to a high-voltage network, and the disadvantage is unreliability. The other types also have their pros and cons.
Parallel connection
A light-emitting diode (LED, LED ) is a micro-element, the operation of which depends on many parameters. Errors in microtechnology lead to the fact that the volt-ampere characteristic of each individual LED is different. Therefore, the threshold of operation ("switching on") of all diodes at the same time is different. This is allowed by quality standards and must be taken into account when building electrical circuits. Parallel connection of LEDs requires exactly this setting for their simultaneous actuation.
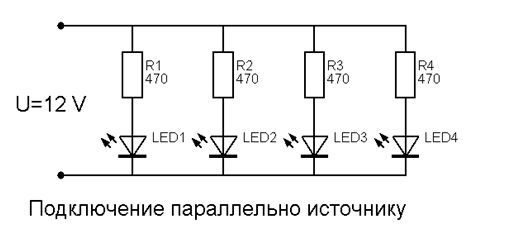
In the wiring diagram you can see that a different resistor is selected for each LED. When tuned, the resistors R1-R6 regulate the operation of the entire system. The operating threshold of each diode is between 2.5 and 3.0 volts, so the resistors must be selected for each diode.
A positive indicator is the low-voltage characteristic. The actuation level of a single LED is up to 3.0 V, so you can calculate the entire light assembly for low voltage.
A significant advantage of the parallel connection is the "survivability" of this option. If one LED element fails, the system continues to work and give light.
This quality is used in mini-devices, when miniaturization is important and they are assembled on battery "pills". Such crafts are widely available in industry and are designed for small tasks - local lighting, promotional purposes, etc.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages The advantages of the parallel connection are: low supply voltage of the circuit, which makes it possible to build miniature devices; high "survivability" of the system, since each diode is connected directly to the current source. Disadvantages - The need to configure each diode, which increases the number of elements (resistors); the need for a separate current source (or driver) when using general-purpose power grids.
Serial connection
When the LEDs are connected in series in the circuit, the individual circuit settings of each LED individually are excluded. But there are some peculiarities.
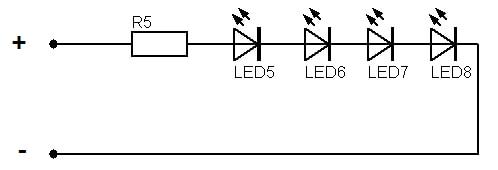
The circuit is tuned with a single resistor, and all diodes are actuated simultaneously. The advantage of this connection is small and simple. The disadvantage is low "survivability": if one diode fails, the whole system shuts down.
The serial method of connecting LED devices allows the use of high-voltage power sources. Typically, these are stationary lighting fixtures for various purposes, using standard public mains.
LED systems with 12 V voltage
LED devices designed for 12 V, usually belong to the class of car lights. Car network has stabilizers, so there is no need for voltage equalization. LED lighting in cars has become popular - many companies widely use LED lighting in models for road lighting and alarm operation, highlighting the interior, trunk and dashboard. However, the use of LEDs in cars has led to an increase in the price of lighting elements, especially head lights and signal light units. In some premium models, the cost of the headlight block is comparable to the price of an inexpensive car.
Also, 12-volt LEDs are used in construction and residential decoration. Often these are LED strips that not only illuminate the room, but also create light installations. This requires the installation of step-down transformers or drivers connected to the house power grid and ensure the long life of the diodes.
220 V LED systems
Such diode systems are the most common. LEDs in series connection, designed for 220 V, are used for lighting large rooms, used in powerful spotlights, in street lighting, signaling systems of airports, etc.
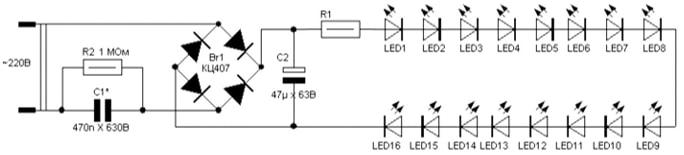
The above version of the serial connection to 220 V is the simplest way to connect a chain of diodes with a small number of components.
Mixed LED connection
This type of connection uses the advantages of parallel and series connection of LEDs. Mixed (or hybrid) connection is used in complex LED systems with a large number of light points and combining high-power narrow beam luminaires and diffuse light.
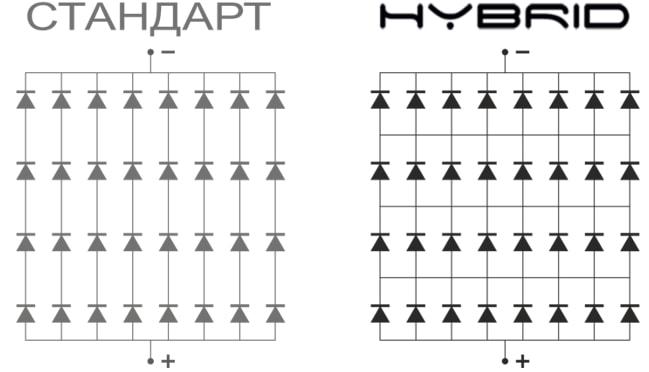
Mixed connection realizes the advantages of parallel and series connection to increase the reliability of the whole system: if one diode burns out, the whole circuit remains functional, while the remaining LEDs are not subject to overvoltage and preserve the resource.
Common connection mistakes
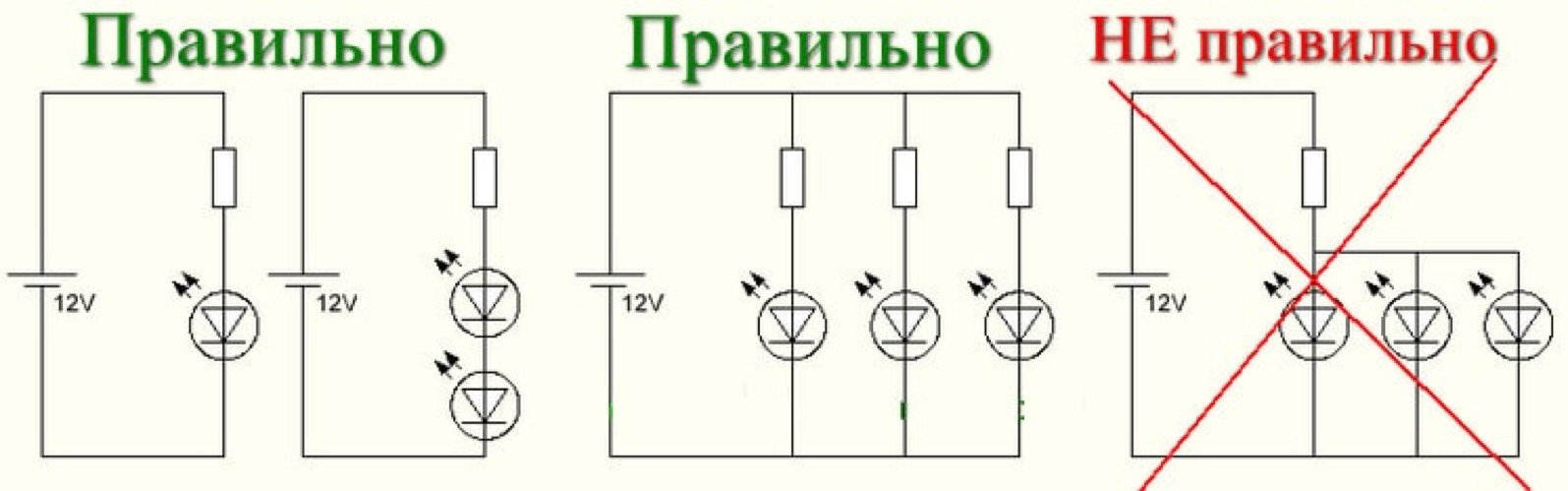
LED - it is a current element, which "painfully" reacts to increases in the flowing current. This should be taken into account when creating systems that include LEDs, where there are a lot of elements that affect the operation of diodes and their life span. This is a common mistake and applies to LED systems on batteries: if the battery is not powerful enough, the current flow is limited by its internal resistance, which will not exceed the limits of the current characteristics of diodes and will not lead to their failure.
For systems that include diodes, diodes with series connection are considered the best. They are simple to design and manufacture, low-cell, reliable in operation, and provide connection to high-voltage sources without the use of step-down transformers.
Of course, systems with parallel connection have the advantage of being able to be used in miniature devices. But they require low-voltage current sources.
To increase the reliability and service life of LED systems, stabilizers and drivers are used to avoid design errors and enable all types of connections.
Topical video: Why diodes are connected in series and parallel.
Choosing the right driver
Drivers are electronic power supplies used when connecting diodes that are sensitive to overcurrents. These devices are mainly based on the principles of pulse-width modulation (PWM), which provides maximum system efficiency and automatic current control. When selecting the right driver for the LED circuit, the following are taken into account:
- input and output voltage;
- output current;
- output power;
- degree of protection from the environment.
Input and output voltages are the requirements of the network parameters: AC or DC (220 V home network - AC, 12 V car network - DC). The load current is calculated from the number of LEDs and their current data. The output power is determined by the power of the whole circuit. The degree of protection depends on whether the luminaire is placed outdoors or indoors.