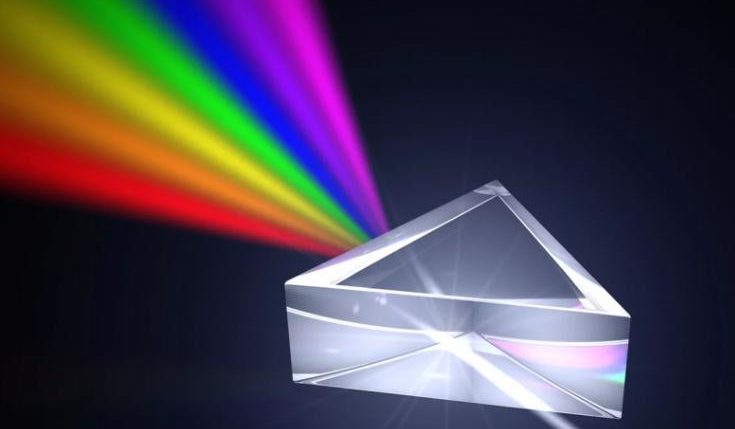
What is commonly referred to as light dispersion
This phenomenon was discovered in 1672 by Isaac Newton. Before that, people couldn't explain why colors are arranged in a certain order when they refract. The dispersion of light once helped to prove its wave nature, but to understand the question better you need to understand all aspects.
Definition
The phenomenon of light dispersion (or dispersion) is due to the fact that the refractive index is directly related to wavelength. Dispersion was first discovered by Newton, but much of the theoretical basis was developed by scientists in a later period.
Thanks to dispersion, it was possible to prove that white light is made up of many components. To explain simply, a colorless ray of sunlight when passing through transparent substances (crystal, water, glass, etc.) is decomposed into the colors of the rainbow of which it is composed.

As a result of light from one substance to another, it changes direction, which is called refraction. White contains the entire range of colors, but this is imperceptible until it is subjected to dispersion. Each of the compound colors has a different wavelength, so the angle of refraction is different.
By the way! The wavelength of each of the colors of the spectrum is constant, so when passing through a transparent substance, the hues always line up in the same order.
The history of Newton's discovery and conclusions
The story goes that the scientist first noticed that the edges of the image in the lens are colored in the period when he was engaged in improving the design of telescopes. This greatly interested him and he set out to discover the nature of the appearance of colored fringes.
At that time in Britain was an epidemic of plague, so Newton decided to go to his village Woolsthorpe, to limit the circle of communication. And at the same time to conduct experiments to find out where different shades come from. To do this, he grabbed some glass prisms.

During the period of his research, he conducted many experiments, some of which are conducted in unchanged form to this day. The main one was as follows: the scientist made a small hole in the shutter of a dark room and placed a prism of glass in the path of the light beam. The result was a reflection in the form of colored stripes on the opposite wall.
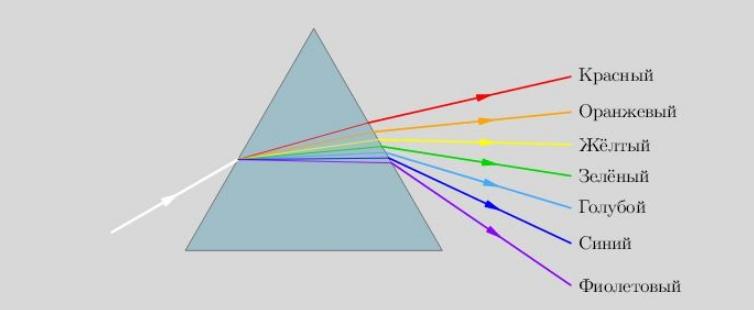
Newton isolated red, orange, yellow, green, blue, blue and purple from the reflection. That is, the spectrum in its classical sense. But if you take a closer look and isolate the spectrum with modern equipment, you get three main zones: red, yellow-green and blue-violet. The others occupy insignificant areas in between.

Where it occurs
Dispersion can be seen much more often than it first appears. You just have to pay attention:
- Rainbow - is the most famous example of dispersion. Light is refracted in the water droplets, resulting in a rainbow, which experts call the primary rainbow. But sometimes light is refracted twice and a rare natural phenomenon appears - a double rainbow. In this case, inside the arc is brighter and with a standard order of colors, and outside - blurred and the shades go in reverse order.
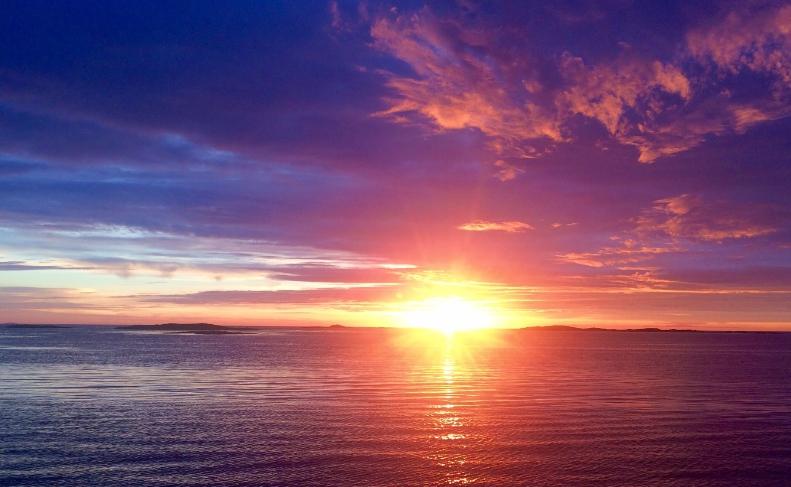
- Sunsets., which can be red, orange, or even multicolor. In this case, the object refracting the rays is the Earth's atmosphere. Due to the fact that air is composed of a certain mixture of gases, the effect is different and can be different.
- If you look closely at ...at the bottom of an aquarium or a large body of water... with clean, clear water, you can clearly see iridescent reflections. This is due to the fact that the solar spectrum spreads out into the entire color spectrum by diffusion.
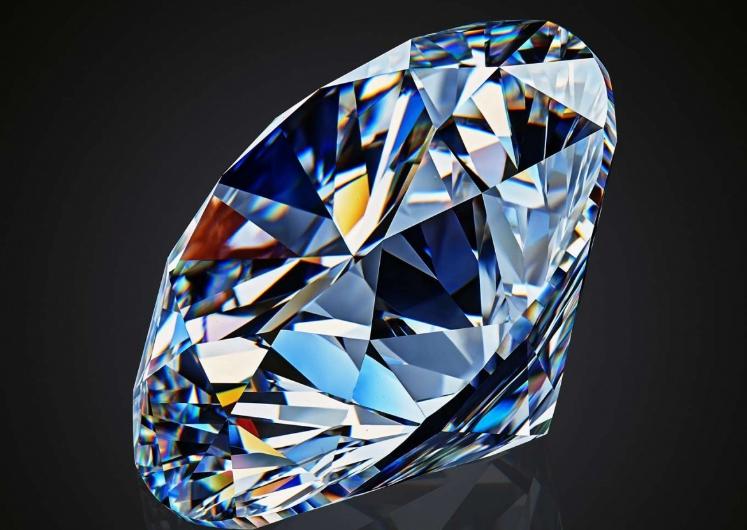
- Gemstones jewel-cut gems also shimmer. If you rotate them carefully, you will notice how each facet gives a different hue. This phenomenon can be seen on diamonds, crystal, cubic zirconia, and even on glassware with good cut quality.
- Glass prisms and any other transparent elements will also produce an effect when light passes through them. Especially if there is a difference in light.

To show children the phenomenon of dispersion, you can use ordinary soap bubbles. Pour the soap solution into a container, and then lower any appropriately sized wire frame. After removing it, you can observe iridescent overflows.
Decomposition of light into a spectrum is also easy to do with a smartphone flashlight. In this case you need a glass prism and a sheet of white paper. The prism should be placed on a table in a dark room, with a beam of light on one side and a piece of paper on the other side, it will have colored stripes on it. Such a simple experience is very appealing to children.
How the eye distinguishes colors
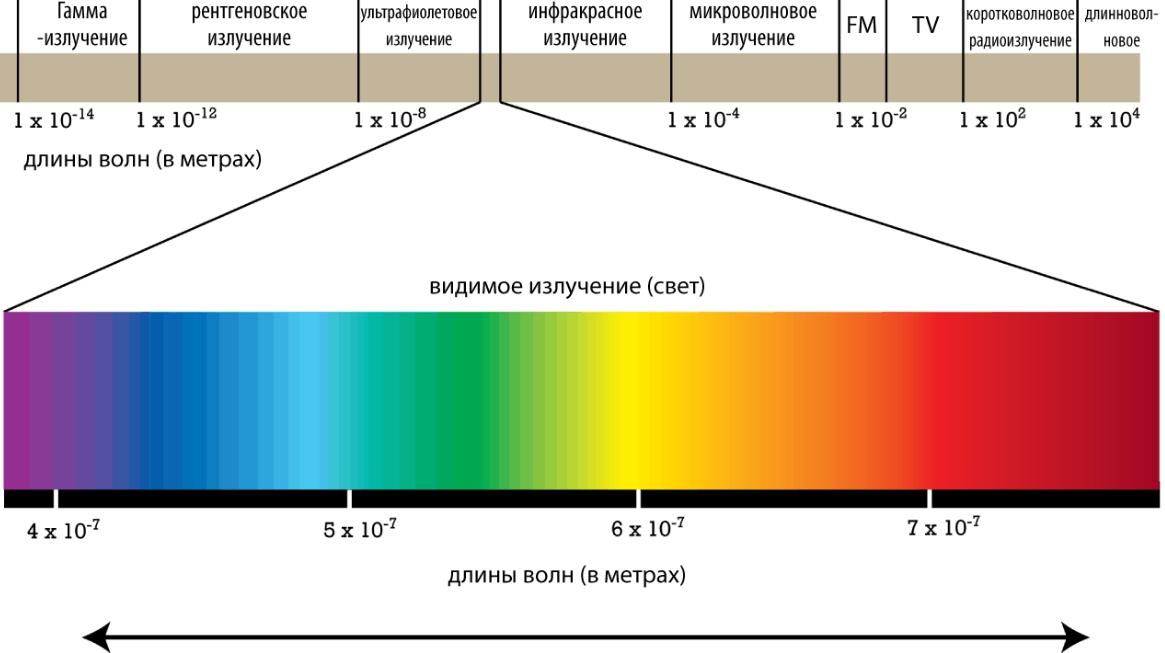
Human vision - a very complex system that can distinguish between parts of the electromagnetic spectrum. The human eye recognizes wavelengths from 390 to 700 nm. The electromagnetic radiation in the visible range is called visible light or just light.
Colors are distinguished by rod cells and bulb cells in the retina. The first type has high sensitivity, but is able to distinguish only the intensity of light. The second distinguishes colors well, but works best under bright light.
The cone cells are divided into three types, depending on which wavelengths they are more sensitive to - short, medium or long. Thanks to the combination of signals coming from all types of cones vision can distinguish the available range of colors.
Each type of cell in the eye can perceive not a single color, but different shades in a large wave range. This is why vision allows us to distinguish the smallest details and see the diversity of the world around us.
The dispersion of light once showed that white is a combination of the spectrum. But you can only see it after its reflection through certain surfaces and materials.