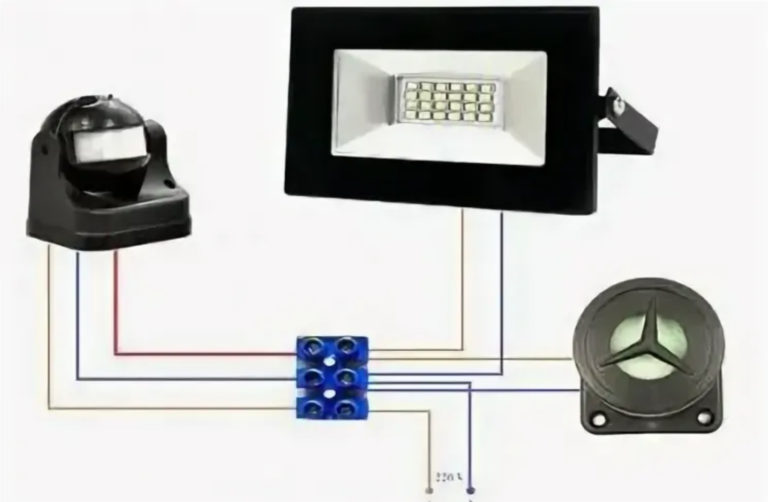
Design and operation of motion sensors
A motion sensor (sensor, detector) is a device that detects the presence of moving objects in the detection area without contact. Most of these sensors do not respond to motion, but to the appearance of new objects. But the name is well-established and widely used.
Areas of application
Motion detectors are used in various areas of automation. In each area a different variety of sensors is preferred.
Security systems
The most logical application of motion detectors is in systems facility security systems. The sensor can detect an intrusion into a protected area or room and sound an alarm or activate additional devices.

Switching on standby lighting
In places where people are not regularly present, these sensors can save a great deal of energy. These areas include entrances to residential and industrial buildings, warehouses and other areas. Lights in them need to be turned on only for the time when the occupants or personnel are present. When a sensor detects motion, it generates a signal to activate the lights.
Smart Home Systems
In Smart Home systems, you can find a much wider application area for detectors than simple lighting control. A signal from a sensor can control heating, ventilation, air conditioning and other engineering systems. The mode of operation changes depending on the presence of people in the monitored area.
Motion sensor and door opening from Aliexpress (Smart Home system).
Varieties of sensors and technology of their work
Motion sensors are built on different principles. Each type of motion sensors has its own pros and cons, determining the scope of the devices.
Infrared sensors
The most common sensors are those that capture infrared radiation. They belong to passive sensors - controlled space is not "illuminated" by corresponding signal. In the simplest case consists of two lenses that focus light radiation (infrared radiation has the properties of light, although invisible to the naked eye) from the two zones of the controlled room. The lenses are directed so that the zones do not overlap. In normal mode they receive radiation of the same intensity. If a person or other warm-blooded creature appears in one of the zones, the level of radiation increases, which is "seen" by one of the sensors - in whose zone the object is located. The comparison circuit sees the difference in intensity. When a certain level is reached, an alarm is generated.
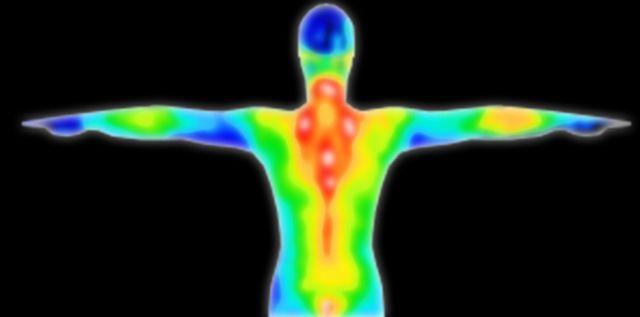
In practice, two zones are not enough for reliable noise immunity, and the viewing sector is divided into a large number of subsectors by means of several lenses. In fact, this sensor is a presence detector - it will register the presence of a person, even if he is immobile. The disadvantages of such a device are considered a tendency to false alarms due to thermal interference (jets of heated air, local heating due to changes in lighting, etc.).
Ultrasonic detectors
The principle of operation of this motion detector based on the phenomenon of echolocation. The transmitter generates sound waves that are inaudible to humans. After a series of transmissions, the detector enters the reception mode. If there are no moving objects in the viewing area, the ultrasonic signal reflected and returned to the sensor will have the same frequency as the emitted one. If the signal is reflected from a moving object, the frequency of the returned ultrasound will be different (Doppler effect). The circuit analyzes the parameters and, if motion is detected, generates an alarm. Such a sensor is more immune to interference due to the fact that it reacts only to moving objects regardless of their nature and temperature. But it is unable to detect slowly moving objects - they will not shift the frequency within the necessary limits.
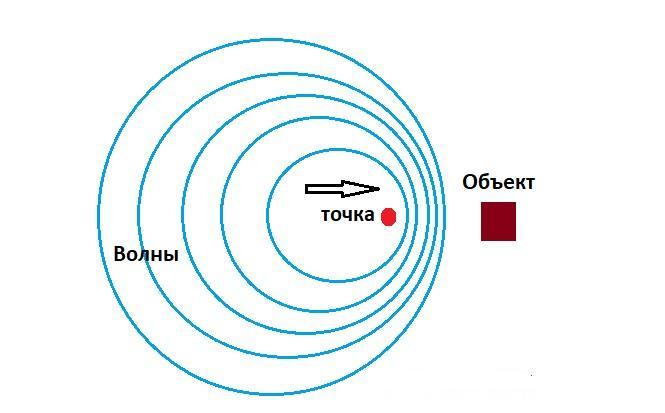
Radio Frequency Sensors
This type of sensor also acts on the locator principle, but operates at radio frequencies. The emitted signal must have a high enough frequency to detect small objects. The Doppler effect is not used in such conditions - to get sufficient shift, objects must move at a speed comparable to the speed of light. Therefore, the sensors only detect changes in intensity and are also in fact presence detectors. Such a detector will be triggered when objects reflecting the signal appear (or disappear) in the area, regardless of whether they are moving or not.
The advantage is the ability of the signal to penetrate through radio-transparent (wooden, brick, etc.) walls and partitions, so they can be used to control large rooms with several rooms. The disadvantage is the high cost of the device, as well as the inability to detect objects that do not reflect radio waves. Another limitation for use is the effect of radio radiation on living organisms. The signal level must be minimized.

Combined systems
For reliability, you can combine two or more principles of detection of an emergency situation in one sensor. In security systems, the infrared sensor is often combined with a glass break detector or an acoustic relay. This allows you to reliably detect unauthorized entry into the apartment and avoid false alarms.
Another option is a combination of motion sensor and photo relay. Such a system turns on the light in the entrance hall when a person is detected, but only at night. During the day, the photo relay turns off the detector, so as not to waste energy during daylight hours.
Popular outdoor surveillance cameras with motion detection sensor. The system is activated only when an object enters the field of view of the complex. It has two advantages:
- The recording is made only at the moments you need, which saves space on the storage device;
- Review and analysis is facilitated by not having to look through long uninterrupted periods of time.
There are other ways to combine sensors. This approach can improve the performance of object detection systems.
Parameters for selecting sensors
Part of the characteristics of the motion sensor applies to any device powered by electricity. These are the degree of protection, supply voltage, dimensions, type of mounting, etc. But there are also specific parameters that only this category of detectors has. It is these characteristics that are most important to give a description.
Viewing angle
The viewing angle depends on the design of the sensor. Ceiling sensors have a 360-degree diagram and "see" the whole room.
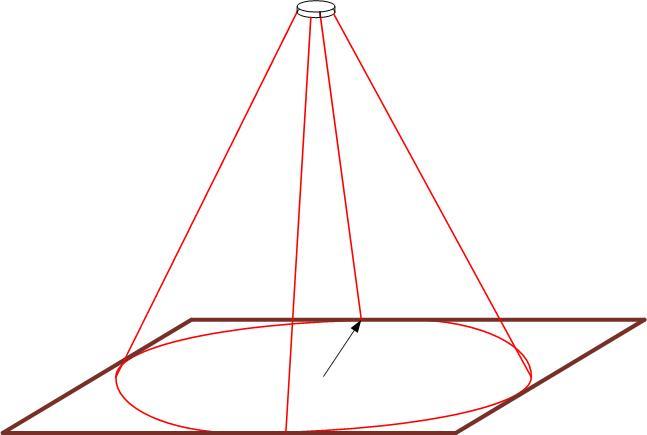
Wall sensors have a smaller angle of view by virtue of their design - from 120 to 180 degrees.
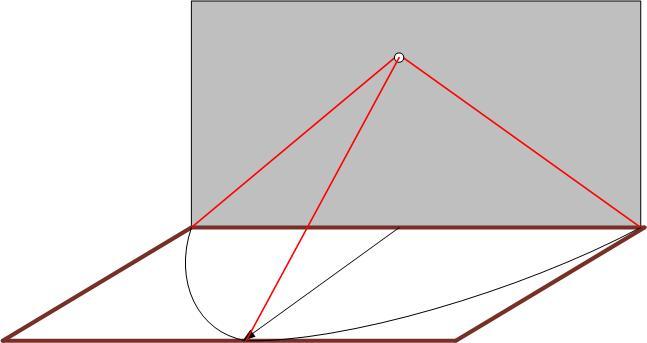
Immediately below the sensor is the invisibility zone. An intruder can sneak up on the sensor and damage it, making the detection system inoperable. To avoid this, you should choose a sensor with an additional sector of view - anti-sneaking or anti-vandal.
Detection range
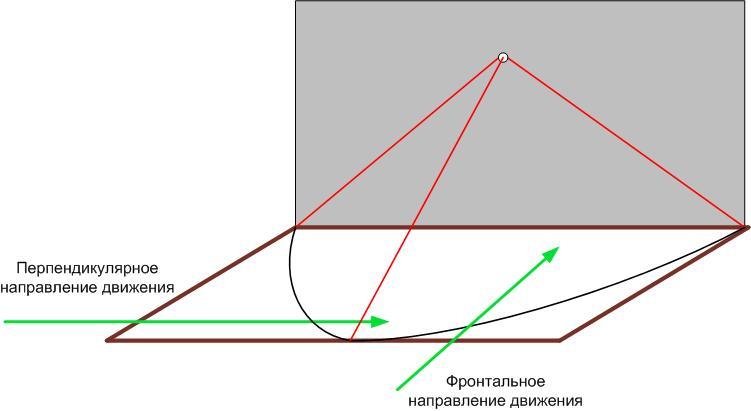
The range depends on the design of the sensor. But remember that the distance at which the sensor can detect a moving object depends on the direction of movement. Most sensors are most sensitive if the movement is tangential to the circle in the center of which the sensor stands (perpendicular distance). The lowest sensitivity is when the object moves in the direction of the detector (frontal or radial distance). In the first case, the range will be greater. The opposite is true for ultrasonic devices. This is due to the different degree of manifestation of the Doppler effect in different directions. Manufacturers do not always indicate this difference in the specifications, especially for inexpensive devices. One figure can be found in the specification - and it is on the conscience of the manufacturer.
| Type of device | Working principle | Declared range, m |
| DD-024-W | Infrared | 6 |
| Steinel US 360 COM2 | Ultrasonic | 10 in radial direction |
| MW32S Black | Microwave | 6 |
| MW03 | Microwave | 8 |
| IEK DD 008 | Infrared | 12 |
Place of use
The place where the equipment can be used is mainly determined by the degree of protection. Indoors the IP may be minimal. Outdoors, the detectors must be protected from dust and water penetration. Also the choice of location can be influenced by the method of attachment.
Video overview: Internal device and purpose of the Finder motion detector.
Additional functions
To improve the performance of the system, increase its efficiency and avoid false alarms, detectors can have additional functions. We have already mentioned the photorelease, which allows you to put the system out of operation during daylight hours, as well as an additional sensor for stalking zones. But this list of auxiliary options is not exhaustive.
Light-off delay
Sensors equipped with a luminance relay may have a useful function. When a moving object disappears from view, the lights are not turned off immediately, but after a delay of a few tens of seconds. Minor overconsumption of electricity pays off with convenience - a person can leave the area of the detector, but not permanently leave the monitored area. With this feature, he will not do it in the dark.
Protection from animals
It is not uncommon for small animals to cause unauthorized activation of the sensors. When they appear, turning on the lights is unnecessary, as is the reaction of the guards. Therefore, some sensors are inherently insensitive to the appearance of small moving objects. In infrared sensors, this function is implemented in the form of a limit on the minimum size of the heat spot.
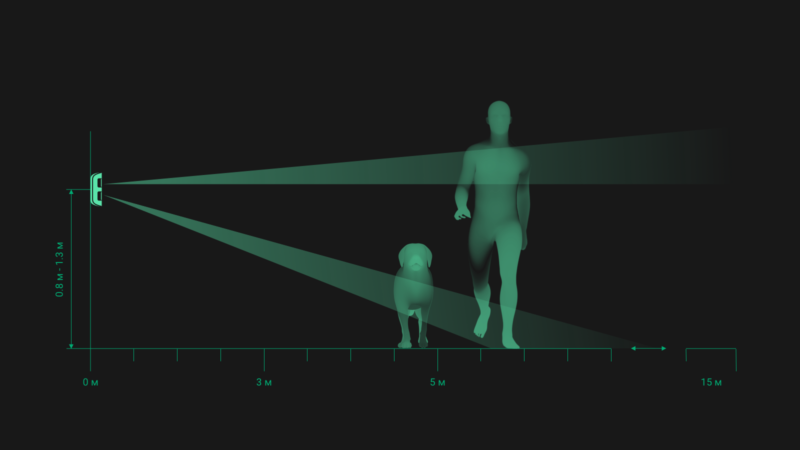

Important! If a small animal moves in close proximity to the sensor, the angular size of the heat spot may be sufficient for a false alarm. Therefore, restrict access to the area around the sensor installation site.
Autonomy
If there are problems with the organization of the power supply of sensors from the domestic power supply network, stand-alone devices can be a good choice. Energy independence is provided by conventional batteries. Many devices from one galvanic cell work for several months. In this case, it makes sense to choose sensors with wireless signal transmission - to get rid of cables altogether.

Motion detectors are universal devices. They can be used to build various security, warning and control systems. Non-standard use of devices is also possible - everything is limited only by imagination and engineering ingenuity.