Features of quartz treatment at home
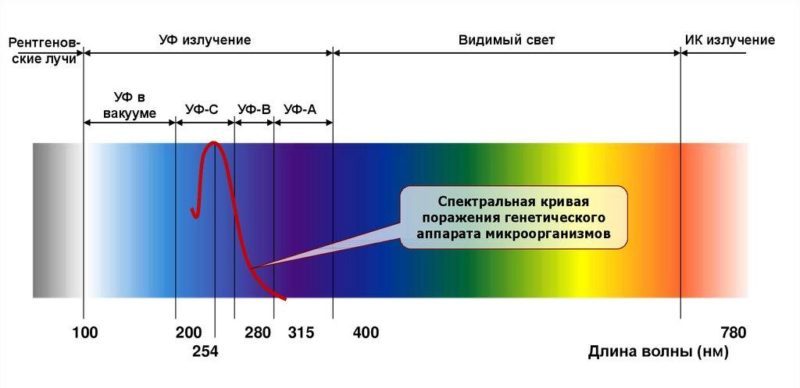
At the beginning of the twentieth century, the main factor reducing the survival rate of hospitalized patients was the so-called nosocomial infection: when, in addition to the underlying disease, the patient contracted a cross-infection from other patients. This occurred both directly from the source, and indirectly, through objects, airborne or air-dust. Against this background, the question arose of finding additional prophylactic measures capable of keeping patients safe. The most effective method was ultraviolet disinfection of rooms, called "quartzization", which essentially consisted of turning on a short-term lamp in the room, emitting a hard ultraviolet light in the range of 180-315 nanometers, destructive to pathogenic (and not only) microflora.
How the quartz lamp works
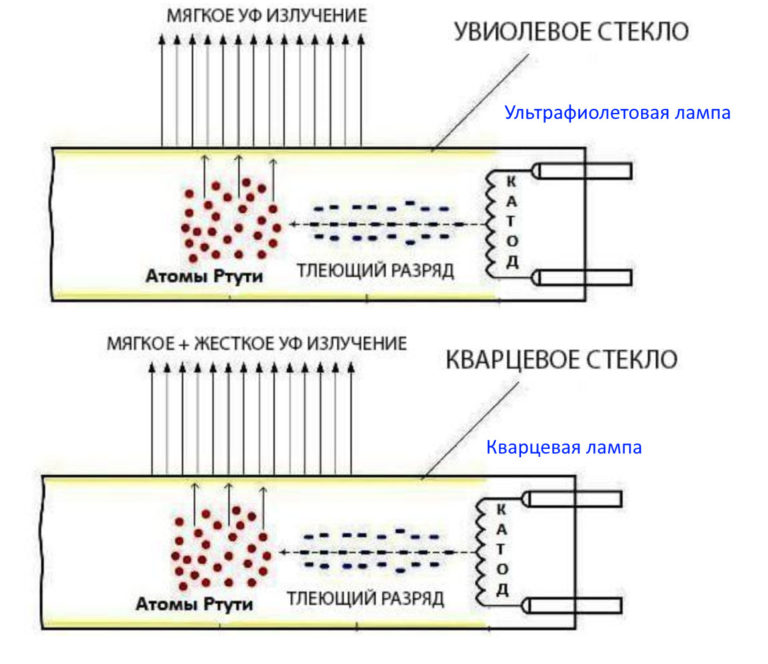
Bactericidal units use a low, medium or high pressure mercury discharge lamp placed in a separate quartz glass bulb as a light source. Ordinary glass also passes through most of the UV spectrum, but retains some of it, which significantly reduces the biocidal effect.
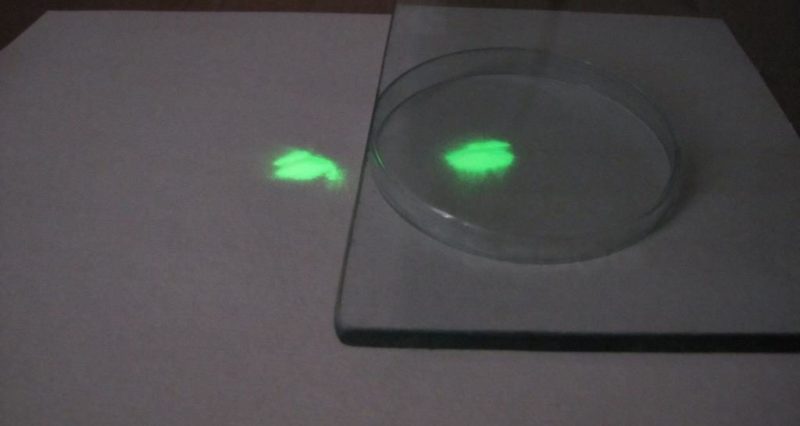
Pay attention! There is a misconception that ordinary industrial glass protects people from aggressive UV radiation, but a number of experiments on the phosphor shows that even under several layers of thick window glass, placed on the glass same Petri dish phosphor under the rays of the UV lamp glows as brightly as without them.

Scientists Köch and Reschinsky in 1906 determined that not all UV light has an equally destructive effect on microorganisms, and experimentally determined the maximum range of biocidal effectiveness between 205-315 nm with a peak at 254 nm.
The prolonged action of the calculated spectrum of light destroys the bonds in the RNA and DNA chains of all known microorganisms: bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa and some types of spores. Many pathogen spores are protected by a tough shell that protects them not only from light, but also from aggressive chemical disinfectants, so the treatment of rooms should be carried out regularly to prevent the reproduction of pathogens from surviving spores. For this purpose, stationary sources of UV light are installed in surgical and maternity wards, infectious disease departments, and bacteriological laboratories for regular and in-line disinfection.

Types
Depending on the design of the installation, there are lamps:
- Open type - when the biocidal effect is provided by exposure to direct or reflected ultraviolet rays.
- Closed type - are installed in ventilation systems or have a type of mobile recirculators, working on the principle of a flow filter with forced air circulation.
Open type of emitters are subdivided into:
- Radial or wide-area irradiation - when the task of the device to cover the maximum area. They are not designed for the presence of people during the disinfection procedure;With a wide spectrum of action.
- With reflected bactericidal flux - when the rays are directed only to the area where personnel are not present, usually in the upper hemisphere.

According to the type of filling of the bulb the devices are:
- mercury - when light is emitted by liquid mercury vapor as charged electrons pass through it;
- amalgam - when mercury in solid form is placed in the bulb. When heated, amalgam vaporizes the mercury vapor, and when cooled, it solidifies again. The efficiency of amalgam devices is higher, and there are far fewer harmful mercury fumes if the glass envelope is damaged, making them relatively safe.
The bulbs of classic quartz lamps are made of quartz and transmit an ozone-forming spectrum from 185 nm. When in contact with oxygen molecules, this light activates the chemical formation of ozone, and for this reason quartz lamps are commonly referred to as ozone lamps. When quartzing in an enclosed space, the concentration of ozone becomes dangerous to the respiratory organs, which means that the room must be ventilated after the procedure. However, concentrated ozone acts as an additional biocide factor, destroying pathogens in places where even reflected UV rays do not reach.
Modern bulbs are already made of uviolet glass or quartz glass, but with a special coating. Such devices do not produce light in the ozone-forming range. Biocidal effectiveness of these devices is slightly lower than that of classic devices, but their safety allows to reduce the training requirements for personnel conducting disinfection in kindergartens, schools, warehouses and even in the home.
How to make your own lamp and quartzing
If an open-type ozone lamp is used, it is necessary to remove pets, fish, plants, and, of course, people from the room before ultraviolet disinfection. You need special goggles with a light filter to protect your eyes, but as a last resort, the tactical yellow polycarbonate goggles will do. They do not hold 100% of all ultra-violet, but they will not hurt your eyes for a few seconds.

To avoid eye damage, it is better to take the button on the device in advance to another room or use a long carrier passed under the door. Quartz treatment of the home room is carried out as follows:
- All biological organisms are removed from the room.
- Open areas of the body are covered with clothing. Protective goggles are worn over the eyes.
- The device is cleaned of dust and positioned so as to irradiate the maximum area, then plugged in and started up.
- The room should be left immediately and closed tightly behind you, preferably with a key, if the design of the door has an interior lock.
- After 25-30 minutes (for non-ozone 30-40), the person in the protection switches off the device, opens the windows for a 15-minute airing.
When carrying out the procedure at home, you should carefully monitor the location of children and animals. It is better to keep them close to you, keeping them busy playing together and children watching cartoons.
The given instructions are suitable for a device that you can make yourself. For this purpose, it is necessary to take Gas-discharge mercury lamp daylight fluorescent lamp with E27 or E40 base, depending on its power, carefully break the outer bulb with a phosphor coating by hitting it lightly with a hammer while pressing the lamp to the wall. It is better to hold the lamp in an upright position with the base facing down. The inner bulb should remain intact, it emits UV rays that make the phosphor on the outer shell glow. Then you need to connect the DRL to the mains, but simply screwing the base into the socket and plugging in the plug will not start the discharge lamp. To start the light source you can go two ways:
- The more appropriate, but complicated and expensive, is to purchase a choke (electronic starter) of the same power as the DRL and put the bulb through the choke according to the diagram, individual for each type of starter, included in the manual of the device. The light from such a emitter will be stable and the life will be long.Lamp CRL lamp connected through a choke.
- The short and simple way is in series connection with DRL You can put an ordinary incandescent bulbwith twice the power of the DRL. That is, if the DRL is 125 watts, then the incandescent bulb should be at least 200, and preferably 250 watts. If you take less, the UV lamp will not be able to work or will not start at all, if more - can burst. The incandescent lamp acts as a choke and will shine simultaneously with the CRL, but the operation of the entire device will depend on the quality of the filament, which at power above 100 watts quickly burns out in our network 220 volts 50 mgts.
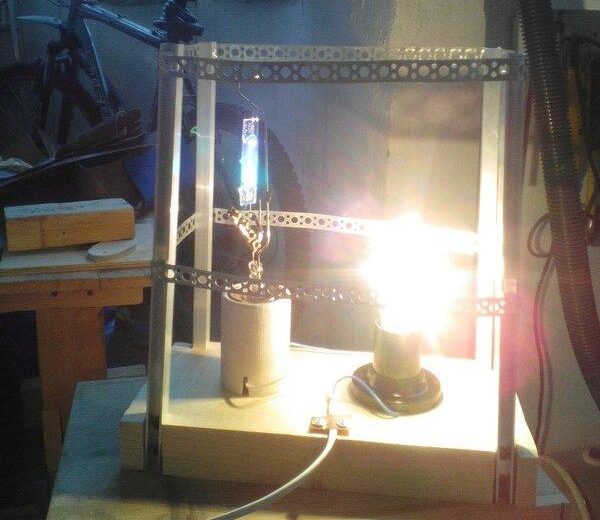

The inner bulb of the FLP, screwed into the socket and connected to the plug in one of the ways should be mounted on a stable stand. It is desirable to protect the glass with a coarse mesh grid or iron protection without a glass plafond from a street lamp. In an upright position, this 125 watt fixture mounted in the center of the room can sanitize a room of up to 25 m2. If it is necessary to set the rays a certain working vector, a metal reflector made of a piece of corrugated aluminum tube cut lengthwise and straightened out is added to the construction of the emitter. The described device is used by gardeners to sanitize boxes before planting spores of edible mushrooms in them, since cultivated fungi are extremely prone to various infections and require aseptic conditions.
Can you stay indoors while quartzing
The use of any quartz lamp of the open type can be either in full protective gear or at a large distance from it at least a few dozen meters, but with eye protection. It is absolutely safe to be in the room without any protection only when using air recirculators, which exclude even accidental exposure to the harsh UV range. It would be safer to exclude being in the room during a device with zonal directionality, as the body receives microdoses of UV radiation due to exposure to reflected light.

Optimal operating time
If there is no patient at home with an airborne or airborne-dustborne infection, the time to quartz the room is chosen based on the schedule of the particular family. It is best done when there are a minimum of family members at home. In some cases it is justified to disinfect and air the bedroom at night and the rest of the rooms in the morning, when most of the family is still resting.
If guests are expected to arrive, bactericidal cleaning should be done both before they arrive, for their safety, and immediately after the potential sources of infection leave, to protect family members who may not yet have had time to become infected directly by the host. However, it was noted that the presence in the house of an unisolated person in a separate room reduces to a minimum the effectiveness of any preventive measures, since the infected continuously infest the air and household items with pathogenic microflora. Reasonable in this case would be to allocate the patient a separate room, located closer to the bathroom and toilet, as an infirmary, where to place a recirculator to protect visitors, and in other rooms to disinfect the usual way.
Do I need to ventilate the room after quartz treatment?
In most cases, it is regular ventilation of the room that gives the best preventive effect if there are infected people in the house. Airing to some extent replaces the action of the ultraviolet recirculator, but is accompanied by a cooling of the temperature in the room, if it is winter. This is the main problem for ozone-forming devices, which must be ventilated after operation.

Periodicity of procedure
The schedule of preventive measures is made on the basis of the epidemic situation or SanPin regulations for each type of enterprise separately. At home during seasonal epidemics, it is acceptable to conduct quartsing every day 2-3 times a day, provided that family members are not exposed even to reflected ultraviolet light. In summer, the procedures are used less frequently, mostly after visiting potential sources of infection with a high contagiousness level. In other cases, wet cleaning followed by ventilation of the room and UV treatment 1-2 times a week is performed.
Lifetime of a quartz lamp
Depending on the type of design, type of gas filler and pressure inside the bulb, the operating life of different germicidal irradiators ranges from 2000 to 15,000 hours. For example, the shortest service life is noted in the high-pressure mercury discharge lamp of 3 kilowatts and more - only 1,500 hours. Low-pressure amalgam-filled bulbs can last up to 15,000 hours. However, much depends on the quality of manufacture of the specific model.
After the life of the device, as a rule, continues to work, but its efficiency may drop to 35-40% of the original. In addition, if the filtering coating on the bulb becomes thin, the device starts to emit aggressive UV-rays in the long-wave range below 200 nm, which becomes noticeable by a sharp ozone odor. To prevent such consequences, it is necessary to record the total hours of operation of the devices in a logbook, as is done in medical institutions.

The specific design of most emitters is such that their resource is used up faster with frequent short-term activations. Therefore, it is better to conduct one disinfection for 30 minutes than two for 15 minutes.
What else you can use the lamp for
Quartzing has found its main use in the home precisely as a disinfecting procedure for such objects as:
- air and surfaces, including bathrooms and storage rooms, where the growth of fungus, mold is noted;Disinfection of restrooms.
- water in swimming pools and storage tanks - for this purpose, the emitter is positioned in such a way as to cover the entire area of the swimming pool. For the disinfection of drinking water tanks, the emitter is installed above the open tank neck. A special submersible or built into the filtration system water disinfection device is used;Water treatment device.
- in agriculture - for example, for sanitation of boxes for cultivation of mushrooms, for screening of eggs in incubators, disinfection of agrarian food products.
In addition, hard ultraviolet acts as a catalyst for curing photocomposite materials in 3D printers, and some types of devices have a narrow therapeutic purpose, such as the "Tubus-quartz" device.

Long-wave UV light is used to identify luminescent elements in forensics, radio engineering, entertainment and commerce, and geology.

The ability of UV rays to attract insects is the basis of the principle of insecticide traps. The soft 380-400 nm range is used in tanning beds.
Please note! Get a tan under a quartz lamp will not work, since the wavelength of 250 nm will cause a burn faster than the activated production of melatonin.
Pros and cons of quartz
Inactivating property of UV rays and the use of bactericidal The inactivating property of UV rays and the use of bactericidal emitters have positive differences compared to the use of chemical disinfectants:
- the ability to treat objects that are not subject to humidification - paper wallpaper, paintings, money;
- absence of chemical reactions and residues of toxic substances on surfaces and in liquid media;
- absence of allergic reactions;
- lower labor intensity of the process;
- a wide range of pathogenic flora affected;
- relative safety.
See also: Does it make sense to use germicidal quartz lamps?
At the same time, the radiation disinfection method is not without disadvantagesThe disadvantages are related to a lack of safety precautions. The disadvantages of using germicidal units include:
- dependence on the availability of electricity in the room;
- brittleness of the emitter bulb and the toxic mercury vapor inside the device;
- requirements for the elimination of living organisms from the room during quartzing;
- limited life span of the device;
- risk of burns skin, mucous membranes and organs of vision during accidental irradiation;
- the risk of exacerbation of chronic diseases and cancer when regularly receiving microdoses of ultraviolet light.
In general, against the background of the spread of airborne infections, the use of biocidal properties of UV radiation is justified as the main and additional means to the standard measures in the form of wet cleaning, airing and quarantine measures.