Characteristics and types of light intensity curve
The light intensity curve refers to the mandatory criteria that manufacturers indicate on the packaging of luminaires. And for different types of equipment are different designations. So it is worth to understand the basic features in order to understand what is meant by the term and what this or that marking means.
What is a light intensity curve
There are several definitions related to the topic. It is necessary to break them all down, so that no questions arise when choosing equipment and determining the peculiarities of its operation:
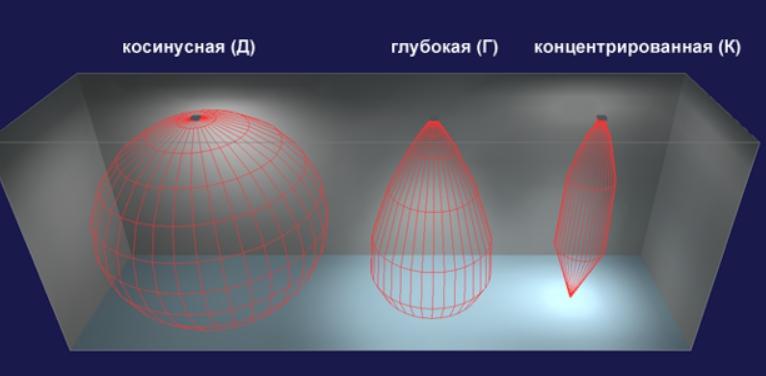
- A light intensity curve is a graph that shows the dependence of light intensity on meridional angles. The image is obtained by dividing the photometric body by a surface or plane. Essentially, the image shows how light will propagate depending on its direction.A visual comparison of the different types of CCC.
- The light distribution of the equipment shows how light will propagate on a given surface. This point is important for the reason that any luminaire distributes light unevenly, so its design is developed so as to direct the maximum flow to a given area. This is done by the configuration of the plafond, reflector, type and position of the lamp.
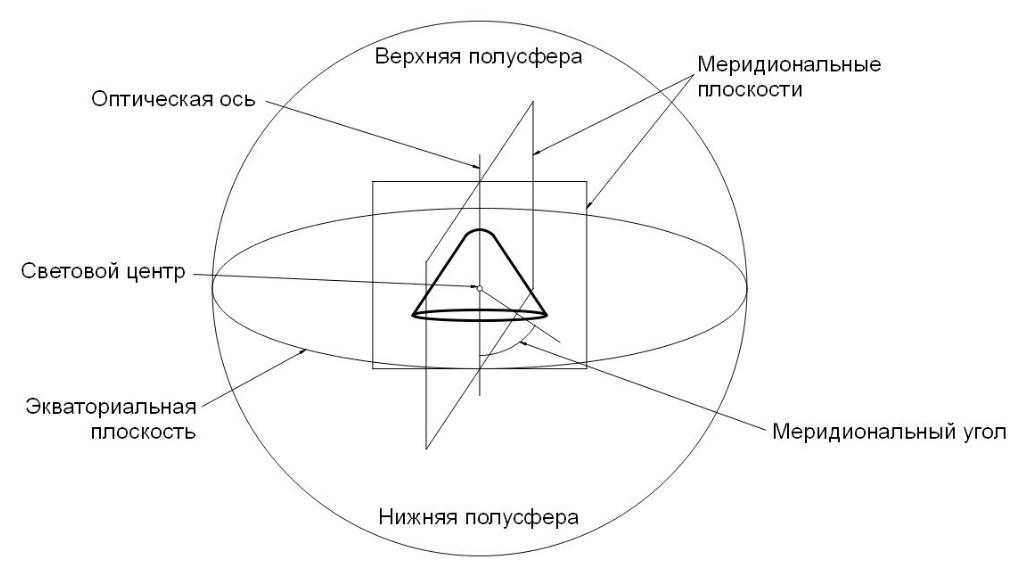
- The optical axis runs through the center of the luminaire or other equipment and serves as the starting point for all calculations. It can be positioned in different ways, it all depends on the plafond and the specifics of light distribution.
- The coefficient of the shape of the light intensity curve reflects the ratio of the maximum illumination in a particular plane to the average.
There are other definitions relating to the topic at hand, but there is no point in sorting them out. The main thing is to always study the graph on the package to understand how light will propagate across the surface.
Types of light intensity curve
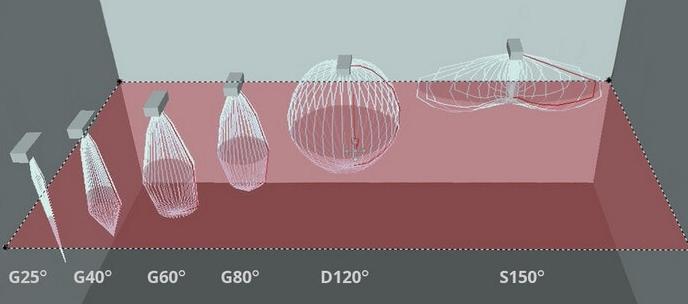
Depending on the propagation light flux There are several basic variants. And each type of light intensity curve is suitable for certain conditions because it has its own light distribution. For clarity, the graph below shows the seven main types of LIDC, for simplicity they are designated by letters.
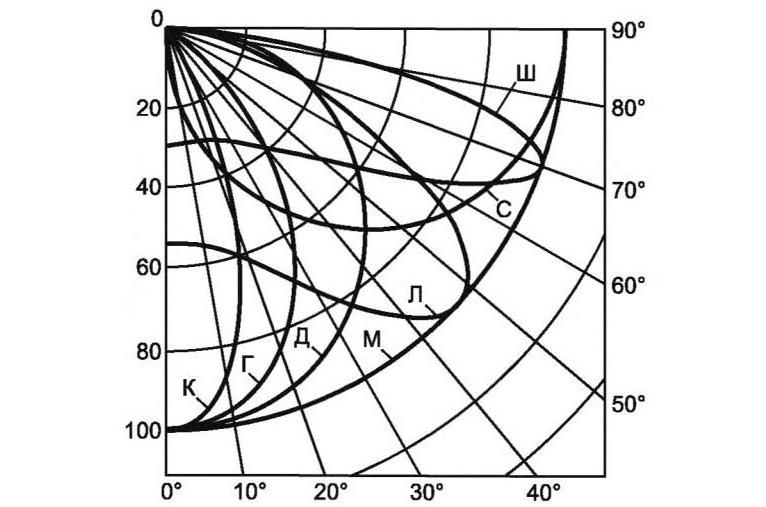
All data is presented in the form of a table with deciphering symbols and diagrams of light propagation.
| Labeling | What does it mean | Angle of light propagation (degrees) | Diagram |
|---|---|---|---|
| К | Concentrated | 30 | 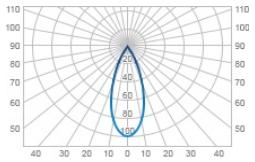 |
| Г | Deep | 60 | 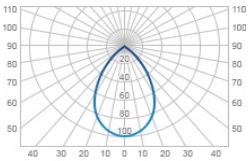 |
| Д | Cosine | 120 | 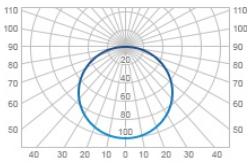 |
| Л | Semi Wide | 140 | 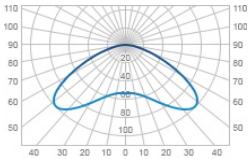 |
| Ш | Wide | 160 | 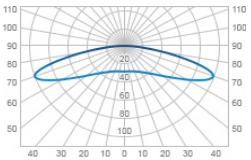 |
| М | Uniform | 180 | 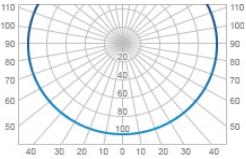 |
| С | Sine | 90 | 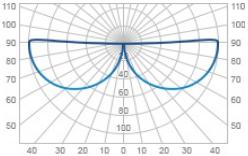 |
There may be other variants, but most often they are used for specific objects with special lighting requirements.
Lighting characteristics of luminaires
In addition to KSS each luminaire has a number of no less important characteristics that you should pay attention to when choosing. The main ones are as follows:
- Light intensity. This is the ratio of luminous flux to the angle of its propagation, measured in candelas.
- Energy efficiency of the light source. The ratio of the electricity consumed to the luminous flux the luminaire provides. It is best to use LED and fluorescent equipment, and traditional incandescent lamps use most of the electricity not for light, but for heating the coil and heat generation.
- Illumination. One of the most important indicators that shows how much luminous flux is per square meter of area. It is this criterion that allows you to choose the wattage and luminaires in the room is not difficult. Measured in lux.
- Color temperature indicates what spectrum the luminaire emits. The values for daylight correspond to from 5500 to 6500 K. Variants with a lower color temperature give a yellowish light, with a higher one - a bluish light. For humans it is best to use a neutral or warm white lightFor humans it is best to use a neutral or warm white light, as this promotes normal day-to-day activities and is less stressful on the eyesight.The color temperature determines the perception of the room.
- Color rendering index (Ra) is measured on a scale from 0 to 100 and tells you how naturally colors are rendered when lighting is used. The ideal color rendering is 100. For interiors, it is worth choosing options from 80 and above to ensure normal perception of the environment.
- Light ripple ratio. Indicates changes in light intensity due to irregular AC power supply. Pulsation can be either noticeable or indistinguishable to the human eye. Pulsation should not exceed 15% for normal operation and rest, and 5% for certain categories of equipment.
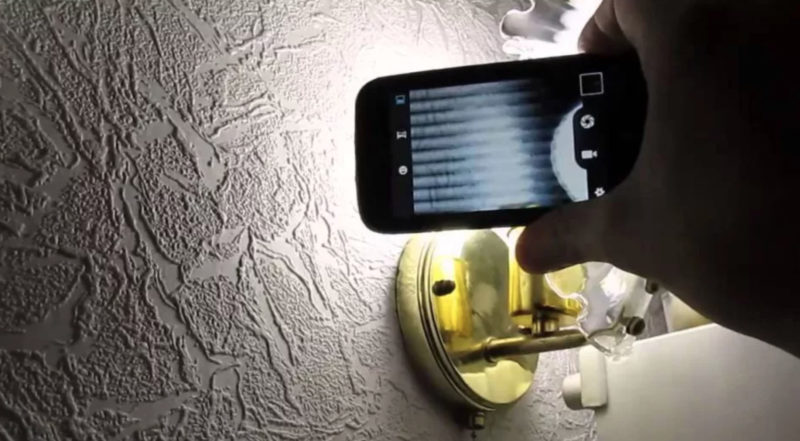

The camera is turned on and the lens is pointed at the light bulb. If stripes are noticeable on the screen, it is better to replace the light source.
How to choose a CCS
To avoid having to calculate the optimal light intensity curve for a particular room or street, you can use general recommendations from experts. It is important to remember the following:
- В living roomsand wherever it is necessary to create a calm and relaxing environment, it is better to install luminaires with a sinus CCS. And you should choose a version with a matte diffuser or diffuser with a plafond that gives reflected light.
- In office buildings, public places, offices and offices a cosine type with a spreading angle of 120° should be used. There are no special requirements, the main thing - pick up the option that provides normal lighting (the minimum standards are in GOST).The larger the angle, the better the light spreads.
- In industrial workshops, on production areasas well as other similar facilities may be used different solutions depending on the specifics of work. The most commonly used variants are "D", "D" or "K".
- As an additional light, as well as for decorative highlighting of certain areas the optimal solution would be a deep CCC. The main thing is to properly adjust the direction of the light flux.
- If you want to highlight a single object, a sculpture, a shelf or a showcase in a storeit is worth using lighting fixtures with concentrated LIDC. It will direct the light flux in the right place, and thus will attract attention.
- For highways, sidewalks and pedestrian areas use lights with a half-wide or wide LIDC. Due to this surface is illuminated evenly without shadows and poorly lit areas. In this case it is very important to choose the optimum height and angle of the lamps.
- In entrances, storerooms, utility rooms and other small rooms equipped with wall lamps, it is worth using versions with a uniform LIDC.
If necessary, different options can be combined in the same room. For example, general lighting in a production hall and additional lights in each workplace.
This video explains the KSS and related concepts in detail.
Finding the optimal light intensity curve is just as important as ensuring good lighting and correct luminaire placement. That's why you need to determine the right branding in advance so you can buy exactly what you need.