The laws of light reflection and the history of their discovery
The law of light reflection was discovered by observation and experiment. Of course, it can also be deduced theoretically, but all of the principles that are used now have been determined and justified by practical means. Knowing the basic features of this phenomenon helps with lighting planning and equipment selection. This principle also works in other areas - radio waves, X-rays, etc. behave in the same way when reflected.
What is light reflection and its varieties, mechanism
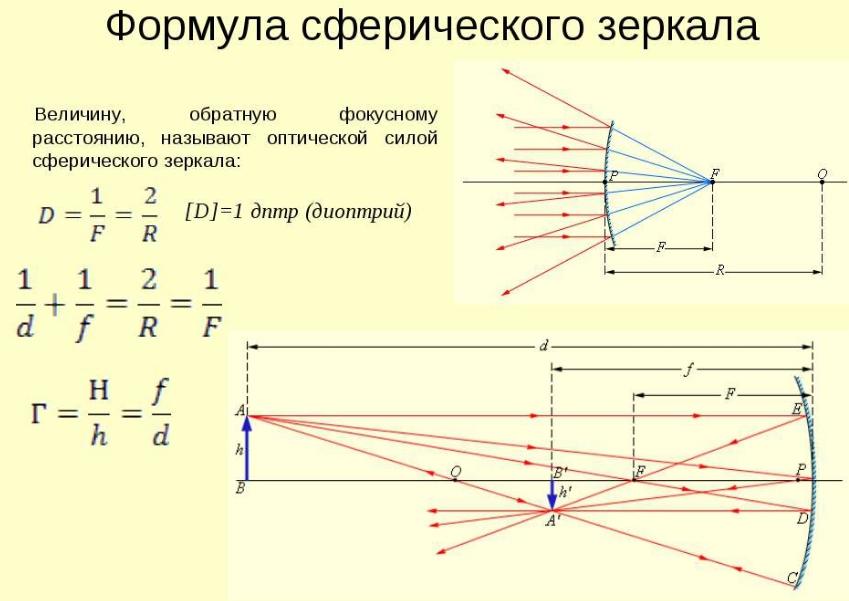
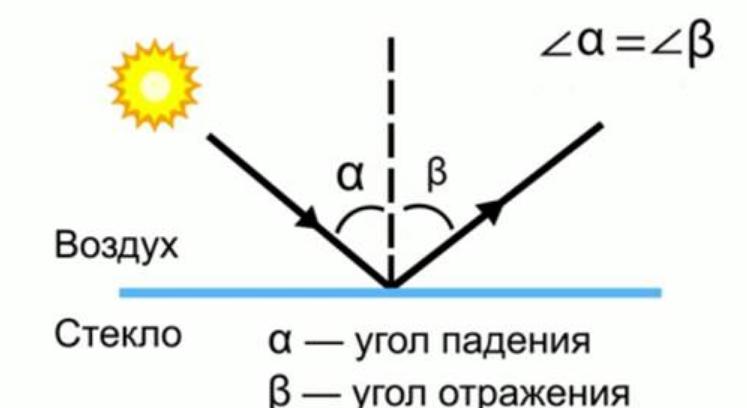
The law is formulated as follows: the incident and reflected rays lie in the same plane, having a perpendicular to the reflecting surface, which emerges from the point of incidence. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Essentially, reflection is a physical process in which a beam, particle, or radiation interacts with a plane. The direction of the waves changes at the boundary of the two media because they have different properties. Reflected light always returns to the medium it came from. Most often during reflection the phenomenon of refraction of waves is also observed.
Mirror reflection
In this case there is a clear relationship between the reflected and incident rays, this is the main feature of this variety. There are several main points characteristic of specular reflection:
- The reflected ray is always in a plane that passes through the incident ray and the normal to the reflecting surface, which is restored at the point of incidence.
- The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection of the light beam.
- The characteristics of the reflected beam are proportional to the polarization of the beam and the angle of incidence. The index is also affected by the characteristics of the two media.
The refractive index depends on the properties of the plane and the characteristics of the light. This reflection can be found wherever there are smooth surfaces. But conditions and principles may vary for different environments.
Total internal reflection
Characteristic of sound and electromagnetic waves. Occurs where two media meet. In this case, the waves must fall from the medium in which the speed of propagation is lower. In the case of light, we can say that the refractive indices in this case greatly increase.
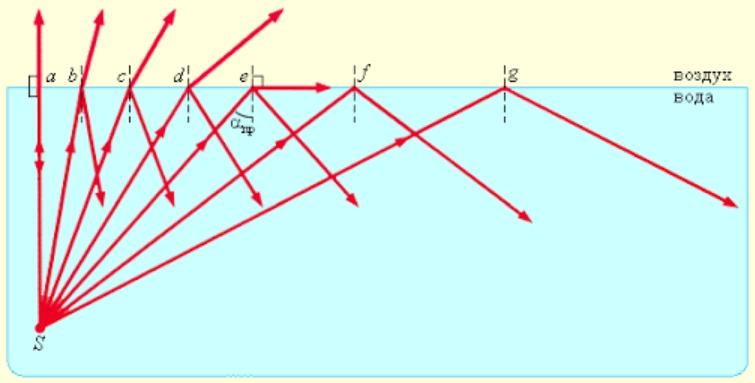
The angle of incidence of the light beam affects the angle of refraction. As its value increases, the intensity of reflected rays increases and the intensity of refracted rays decreases. When a certain critical value is reached, the refractive indices decrease to zero, which leads to complete reflection of the rays.
Critical angle is calculated individually for different media.
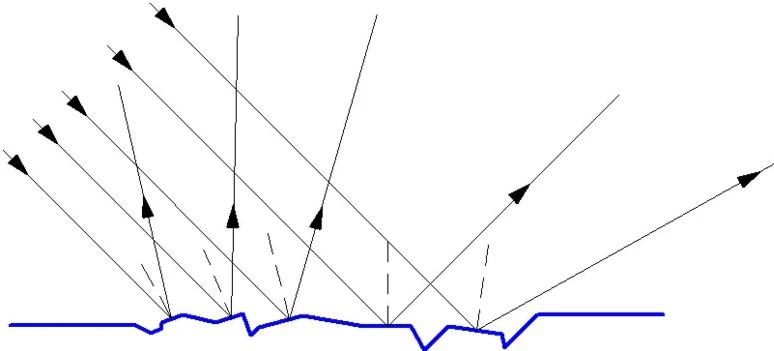
Diffuse light reflection
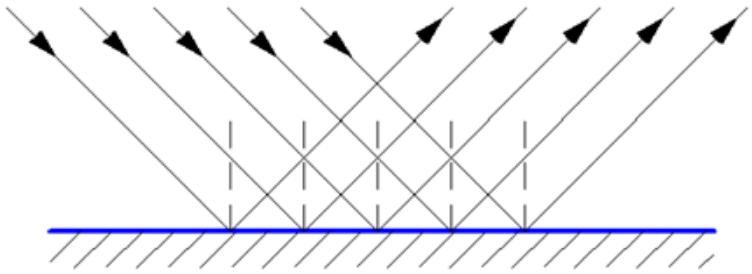
This variant is characterized by the fact that when hitting an uneven surface, the rays are reflected in different directions. Reflected light simply scatters and it is because of this that you cannot see your reflection on an uneven or matte plane. The phenomenon of diffusion of rays is observed when the irregularities are equal to the wavelength or exceed it.
At the same time one and the same plane can be diffusely reflective for light or ultraviolet, but reflect the infrared spectrum well. It all depends on the characteristics of the waves and the properties of the surface.
Reverse reflection
This phenomenon is observed when rays, waves or other particles are reflected back, that is, toward the source. This property can be used in astronomy, natural science, medicine, photography and other fields. Due to the convex lens system in telescopes, it is possible to see the light of stars that are not visible to the naked eye.
It is important to create certain conditions so that the light returns to the source, this is achieved most often through optics and beam direction. For example, this principle is used in ultrasound examinations, thanks to the reflected ultrasound waves an image of the examined organ is displayed on the monitor.
History of the discovery of the laws of reflection
This phenomenon has been known for a long time. Reflection of light was first mentioned in the work "Catoptrics," which dates back to 200 BC, written by the ancient Greek scientist Euclid. The first experiments were simple, so no theoretical basis appeared at that time, but it was he who discovered the phenomenon. Fermat's principle for mirror surfaces was used.
Fresnel formulas
Auguste Fresnel was a French physicist who derived a number of formulas, they are widely used to this day. They are used when calculating the intensity and amplitude of reflected and refracted electromagnetic waves. In this case, they must pass through a clear boundary between two media with different values of refraction.
All phenomena that fit the formulas of the French physicist are called Fresnel reflection. But it should be remembered that all the derived laws are valid only when the media are isotropic and the boundary between them is clear. In this case the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, and the value of refraction is determined by the Snellius law.
It is important that there can be two types of polarization when light falls on a flat surface:
- The p-polarization is characterized by the fact that the electromagnetic field strength vector lies in the plane of incidence.
- s-polarization differs from the first type by the fact that the intensity vector of electromagnetic waves is perpendicular to the plane in which both the incident and reflected rays lie.

The formulas for situations with different polarization are different. This is because polarization affects the characteristics of the beam and it is reflected differently. When light is incident at a certain angle, the reflected beam can be fully polarized. This angle is called the Brewster angle, and it depends on the refractive characteristics of the media at the interface.
By the way! The reflected beam is always polarized, even if the incident light was unpolarized.
Huygens Principle
Huygens was a Dutch physicist who managed to derive principles to describe waves of any nature. It is with his help that both the law of reflection and the ...the law of refraction of light....
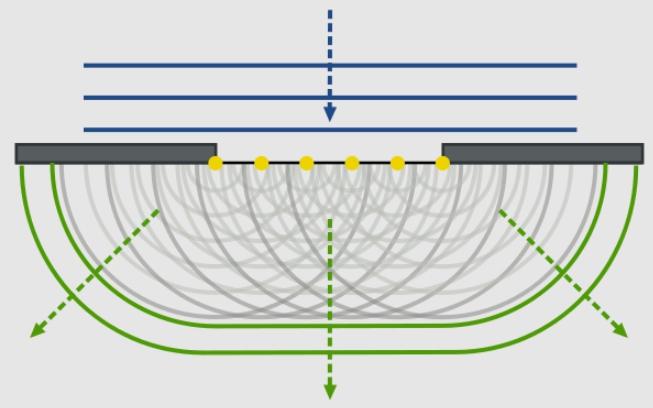
In this case, light is meant as a wave of flat form, i.e. all wave surfaces are flat. In this case the wave surface is a set of points with oscillation in the same phase.
The formulation sounds like this: any point to which the perturbation came subsequently becomes a source of spherical waves.
The video explains the law from 8th grade physics in very simple words using graphics and animation.
Fedorov Shift.
It is also called the Fedorov-Ember effect. In this case, there is a shift in the beam of light when it is completely reflected internally. At the same time the shift is insignificant, it is always less than the wavelength. Because of this shift, the reflected beam does not lie in the same plane as the incident one, which goes against the law of light reflection.
The diploma for scientific discovery was awarded to F.I. Fedorov in 1980.
Lateral displacement of the rays was theoretically proved by a Soviet scientist in 1955 thanks to mathematical calculations. As for the experimental confirmation of this effect, it was done a little later by the French physicist Embert.
Using the law in practice

The law in question is much more common than it seems. This principle is widely used in many different areas:
- Mirror - is the simplest example. It is a smooth surface that reflects light and other types of radiation well. Both flat versions and elements of other shapes are used, for example, spherical surfaces allow you to distance objects, which makes them indispensable as rear-view mirrors in the car.
- Various optical equipment also works thanks to the principles discussed above. This includes everything from eyeglasses, which are found everywhere, to powerful telescopes with convex lenses or microscopes used in medicine and biology.
- Ultrasound machines also use the principle in question. Ultrasound equipment allows for precise examinations. X-rays are distributed according to the same principles.
- Microwave ovens - Another example of the application of the law under consideration in practice. This can also include all equipment powered by infrared radiation (e.g. night vision devices).
- Concave mirrors allow lanterns and lamps to increase their performance. At the same time, the power of the bulb can be much less than without the use of a mirror element.
By the way! Thanks to the reflection of light we see the moon and stars.
The law of light reflection explains many natural phenomena, and knowledge of its features allowed to create equipment that is widely used today.