Description of the main types of light bulbs
It is impossible to imagine modern life without bright electric light. It is a comfort for vision and a great feeling of well-being. Lamps are used at home, in production, underground, underwater and in space. For more than 100 years of development different kinds of bulbs have appeared, working on many physical effects.
Incandescent bulbs.

The advantages of modern incandescent light bulbs (LON) should include:
- the simplicity of design and the low price of the materials used, which in mass production ensure their low cost;
- The ability to create products for different operating voltages - from a few volts to hundreds of volts;
- solid spectrum of luminescence, similar to the spectrum of the sun - it is the spectrum of thermal and visible radiation of metal, heated to luminescence, with this the name of incandescent lamps is associated;
- gas-filled, including halogen incandescent lamps have a lifetime of 2-3 thousand to tens of thousands of hours;
- Dimming is done by fairly simple means - rheostats, thyristor and triac dimmers.
The nominal life of 1,000 hours for LON light bulbs - general-purpose light bulbs - was established in 1930 by an agreement of the world's major manufacturers at the time. Violators of this deadline were and still are punished by international sanctions.
The simplest classification of light bulbs:
- LON - general-purpose lamps, used everywhere in the home and in industry;
- Halogen light bulbs - halogen substances are added to the inert gas;
- Incandescent light bulbs for local lighting, characterized by safe low operating voltage of 12, 24, 36 or 48 V, a short filament and resistance to mechanical stress.
Watch the video to find out how filament lamps are made
More than a century history of incandescent lamps has shown that they can be used in any field of human activity - from household to special lighting:
- in transport - in cars, trains, ships, planes;
- in production - for lighting premises, for obtaining absolutely clean heat without pollutants - in medicine, industry for production of semiconductor devices, in cattle-breeding and poultry - for heating of young animals and many others.
Halogen devices
These sources of artificial light include gas-filled incandescent lamps. They have halogen substances added to the inert gas that fills the bulb - iodine, bromine, chlorine, etc. From the glowing filament, the metal evaporates and settles on the walls of the bulb. In doing so:
- The thickness of the filament is reduced;
- The metal on the glass of the bulb reduces its transparency - the light flux decreases.
Evaporated metal atoms bind halogen substances into "oxides". They, getting on the red-hot metal of the filament body, disintegrate and the metal is deposited on the surface of the filament. As a result, the life of the device increases by 3-4 times, "whiter" shade of luminescence.
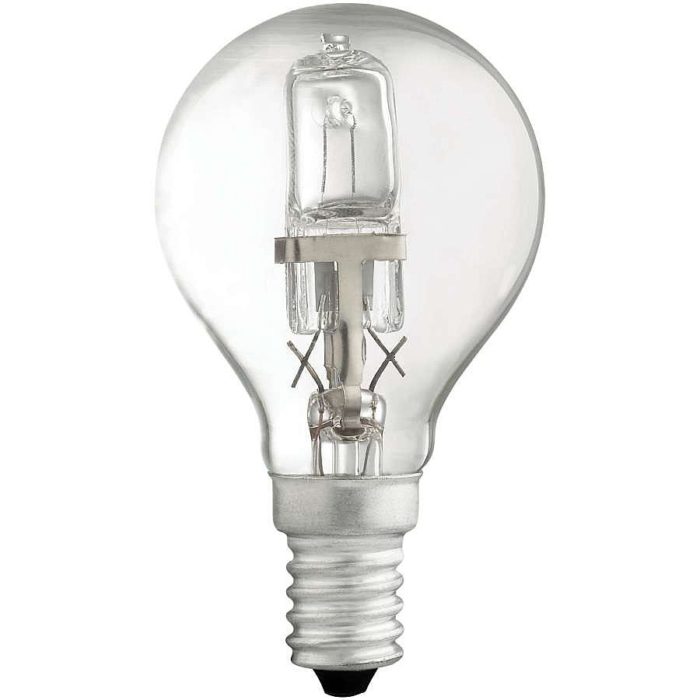

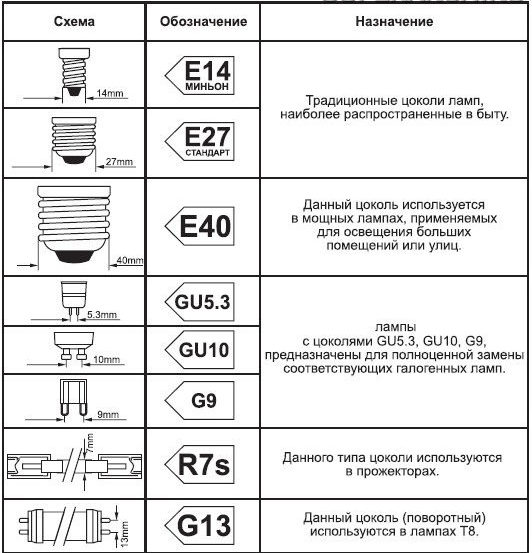
Inside the pear-shaped glass bulb the halogen small bulb is placed on the armature of a conventional incandescent bulb.


G stands for glass, U for "base design", 5.3 for distance between the pin axes in millimeters.
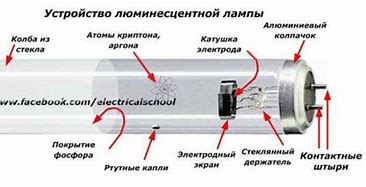
Fluorescent lamps
In a thin-walled glass tube with inert gas and mercury vapor, heated electrodes are placed at the ends, which after heating emit electrons that excite the gas and mercury atoms. Voltage pulses of several hundred volts applied to the electrodes create an electric discharge in the gas. Fueled by the energy of the voltage source, the excited gas and metal vapor atoms begin to emit ultraviolet light. The high energy UV radiation hits the phosphor on the inner surface of the bulb. Under the influence of radiation, the atoms of the phosphor receive additional energy and emit light. Thus in fluorescent lamp The invisible UV radiation is converted into visible light.
Much less energy is needed to produce this flow of light than to heat metal to its melting point.
Tubular lamps are labeled with the letter T and a number that equals 1/8 inch. That is. The T8 type tube is 8/8 inch or 25.4 mm, 25 mm rounded.
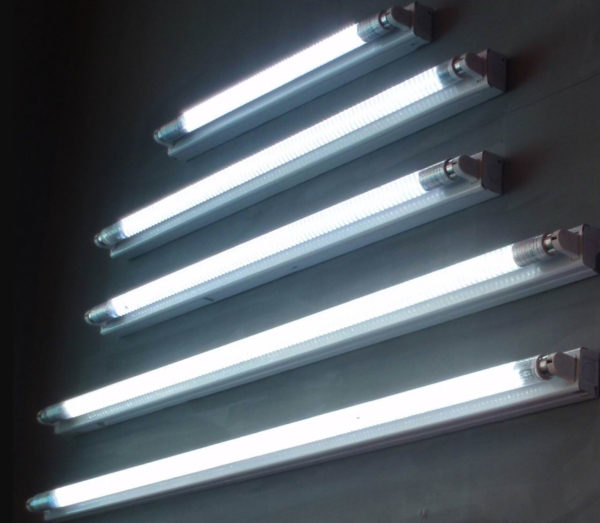

LED bulbs
The basis of a modern LED bulb are super-bright LEDs. The source of light is the process of recombination of electric charge carriers in p- and n-type semiconductor metals - electrons and "holes".
The color of the luminescence depends on the semiconductor material and its doping. The white hue is obtained by converting the blue light of the LED in a yellow phosphor, which is covered with a crystal. Changing the thickness of the phosphor and its composition get any shade of white glow.

Gas-discharge light sources (GDL)
A physical phenomenon used to produce light in Gas-discharge of radiation sources is an electric discharge when a current passes through a gas of a certain composition. Such a discharge is called a glow discharge.
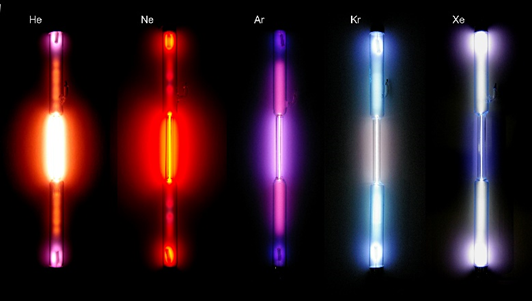
The beginning of the discharge is possible only when the gas is forced to ionize. To do this, a high voltage is applied to the gas in the gap between the electrodes. Usually it is a little more than a hundred volts. During the discharge, the gap between the electrodes breaks down and the current flowing through the gas increases dramatically. A glowing plasma cloud is formed. Its color depends on the composition of the gas in the bulb. For example, neon glows red, argon glows lilac, xenon glows bluish, helium glows red-orange.
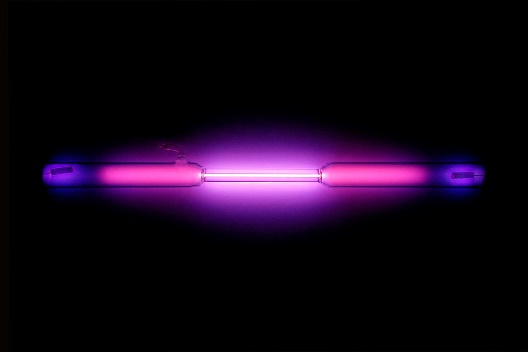
To intensify the luminescence process, a metal, mercury, is added to the air or inert gas in the tube, whose vapors produce ultraviolet radiation. It is re-radiated by the phosphor.
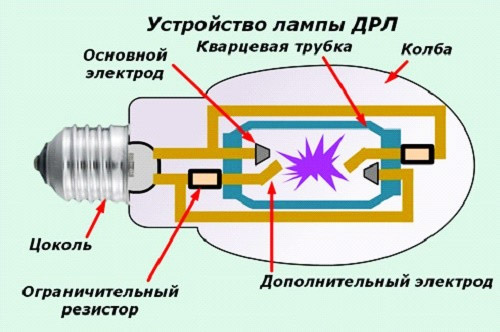
Arc mercury lamp (ARF)
On the basis of this physical phenomenon lamps of the type DRL, DNAT, MFL. These artificial light sources belong to the large category of gas discharge lamps, the arc discharge subcategory.
The abbreviations stand for:
- DRL - arc mercury fluorescent or arc mercury arc lamp;
- DNAT - sodium tubular arc lamp;
- MGL - Metal halide lamp.
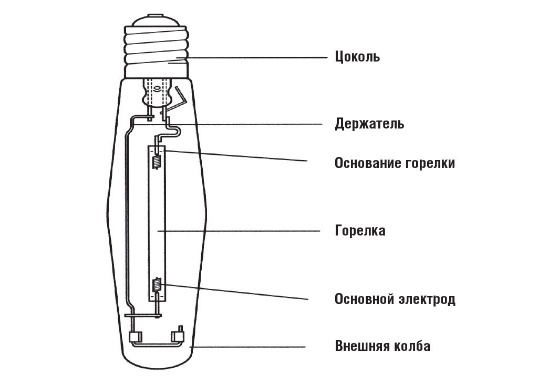
The GFL has a discharge tube mounted inside the bulbs. It is called a torch. The light in a GFL is emitted by a plasma cord or cloud produced by an arc discharge in the burner gas.
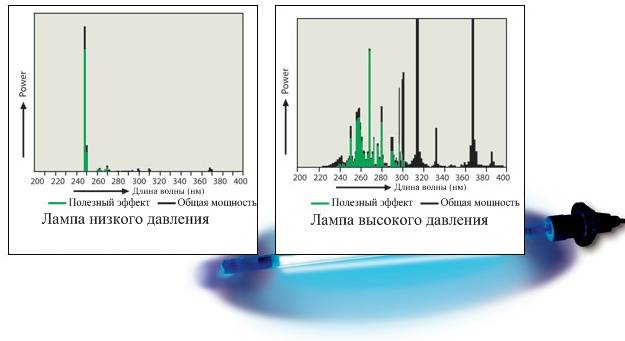
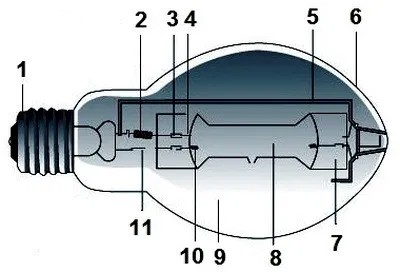
Used for lighting large spaces. For example, plant halls, streets, squares, parking lots, etc.
DNAT lamps

Tubular bulb with a threaded base Edison E40, used in lamps of high power. Discharge tube - burner is visible in the bulb. On the glass of the bulb, near the base, indelibly imprinted with a minimum of characteristics.
In industrial production, the lamp power from 50 to 1,000 watts, but some manufacturers make and 2 and even 4 kW.
The main application is street lighting, roads, highways, underpasses, parking lots. In other words, the places where people are for a short time. The reason is the narrow spectral composition of yellow-orange light emission. Burner made of quartz glass or transparent ceramic. Outer flask of mechanically and thermally resistant borosilicate glass. The flask:
- Stabilizes burner temperature, reducing heat loss;
- Filters excess UV radiation, harmful to the environment and humans.
Metal-Halide (MHL)
One of the types of discharge lamps. They are also called DRI - mercury arc lamps with emitting additives. The construction is similar to DRL. The difference is the addition of sodium, indium and thallium halides in the burner cavity.
MFLs are characterized by high color rendering Ra, aka CRI, reaching 90. At the same time these lamps have a higher light output (energy efficiency) up to 70-95 Lm/W. Service life is not less than 8-10 thousand hours. A variety - DRIZ, which has a mirror layer applied on the inside of the bulb part. This allows, by turning a special cartridge, to direct the flow of light in one direction.
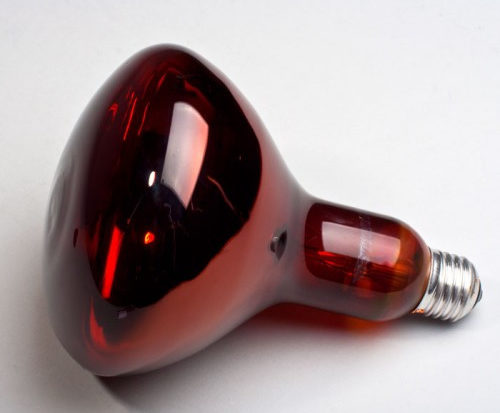
Infrared Devices
These types of The main disadvantage of incandescent lamps, the high level of thermal radiation, has been turned into an advantage. The current is chosen so that the light radiation is less. In it, the filament is heated to a temperature close to the red glow. The main flow of its energy is infrared radiation. It is rightly called thermal. Externally, they look like this.

Kerosene
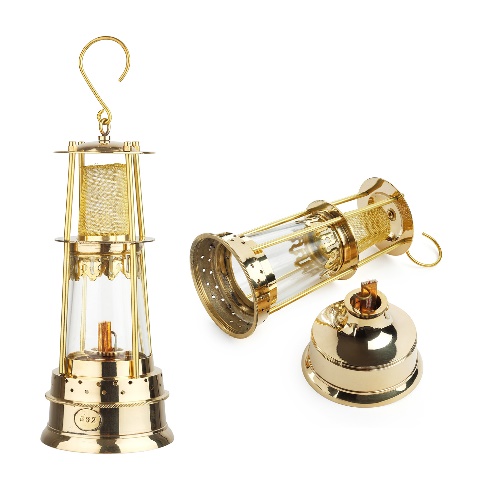

A kerosene lamp. The kerosene tank (right) has a wick dipped in liquid fuel. A protective glass creates a closed volume with elevated air temperature. Cold air is sucked in at the bottom, in the area of the circular container, hot air comes out at the hook-and-loop area.
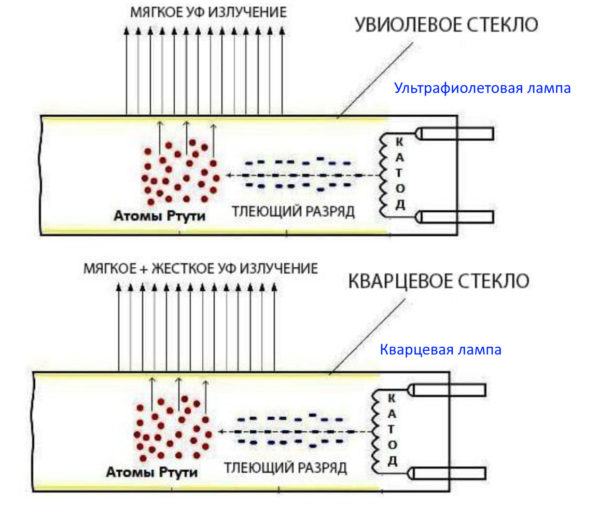
Ultraviolet light sources
The main physical phenomenon in of these of these sources of "light" is an electric discharge in a gas. The resulting ultraviolet radiation is not used to convert into light in the phosphor, but passes through the material of the bulb, made of special violet glass. Externally, such a bulb looks like a black tube. For medical purposes, they are used to disinfect hospital rooms, tools, clothing, and apartments, offices.
Lamp Specifications
Comparisons of different types of lamps are provided by comparing their parameters. Characteristics are divided into such large groups:
Electrical parameters.
These include the operating voltage and power. Operating voltage, unit V (volts) is the nominal voltage at which the lamp consumes the rated power, W (watts), from the mains or power supply. The lamp provides luminous flux, Lm (lumens) with design characteristics.
The rated (operating) voltage and wattage are usually indicated by inscriptions on the top of the bulb and on the side of the base.
Lighting parameters
The main lighting parameters:
- Luminous flux. This characteristic is measured in lumens, Lm (lm). The essence of the concept is the number of units of light falling on a unit of illuminated area.
- Luminous efficacy. Unit of measure Lm/W. The essence of the concept is the amount of light or luminous flux in Lm, which is received from a lamp when it consumes from the mains power of 1 W (W), i.e. Lm/W.
Luminous flux is all the visible and invisible electromagnetic energy emitted by an artificial light source.
Luminous efficiency is the energy efficiency of a light source or efficiency factor. - coefficient of performance.
Operating parameters
The main parameter in this group is the service life. For different types of lamps this life varies. Normal incandescent bulbs have a lifespan of 1,000 hours. But for fluorescent lamps, it ranges from 3-5 to 12-15 thousand hours. The term depends on the manufacturer, the type of lamp, its ECG - The lamp type, its ECG, and the number of times it is turned on and off. For conventional fluorescent lamps, the number of switching on/off corresponds roughly to the number of rated hours of operation of the lamp.
LED lamps have the longest life.. Manufacturers declare theirs from 15-20 to 100 thousand hours. With 3-6 hours of operation per day it's a few years of operation. Over these years the lamp will become obsolete. Or will degrade with a loss of 30-50% of brightness, and often with a change in the shade of luminescence or spectrum of radiation.
Type and size of base
The purpose of the base in a lamp:
- To provide a reliable connection between the light-emitting element of the lamp and the primary power supply circuits, usually the primary AC mains in the building;
- keep the lamp design in a certain position in the lamp plafond and prevent it from touching the plafond, e.g., sconces or chandeliers;
- guarantee a quick change of a burned out lamp and replace it with a new one, etc.
Frequently used:
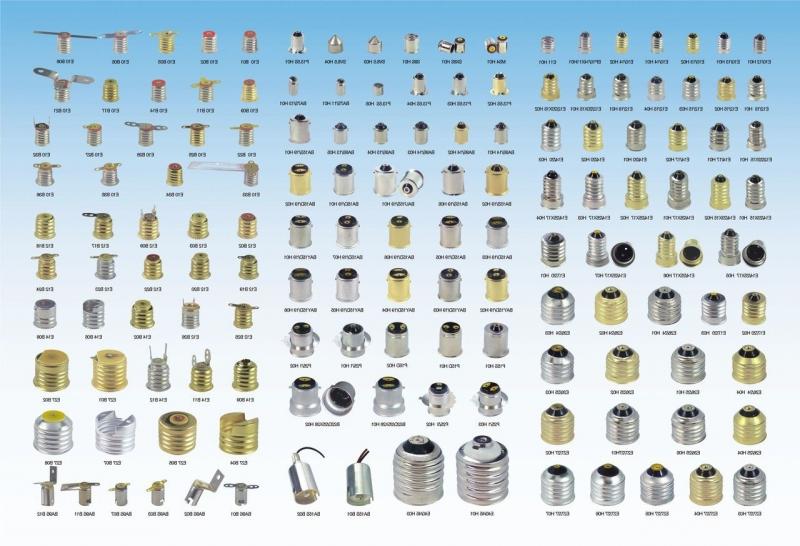
- threaded Edison bases, identified by the letter E and the number indicating the outside diameter of the thread in millimeters, it varies from E5 - bases for micro-small lamps to E40 - for the most powerful lamps, mostly industrial lighting
- pin pins - marked with the letter G, from the word glass, as the pins are "welded" directly into the glass bulb, the figures in the marking of the base - the distance in millimeters between the axes of the pins;
- bayonet or pin - The name comes from the French word "baginet" or bayonet, characterized by not falling out of the cartridge when vibrating, used on vehicles - cars, planes, ships and ships, trains and streetcars, etc. One of the names is Swann's plinth - after the inventor.
Main types of plinths - Edison, pin, Swahn's bayonet, aka pin.
Bayonet plinths have the Latin letter B as the first element.
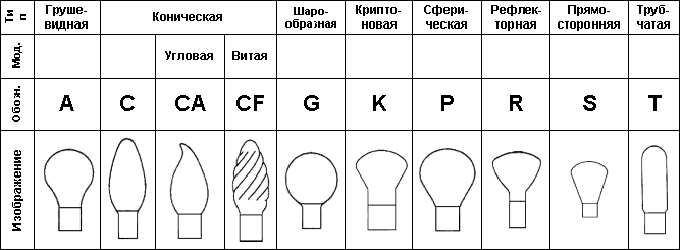
Bulb shape
The forms of bulbs of lighting fixtures are determined not only by its technical essence, but sometimes also related to its origin. For example, bulbs А, С, SA и CF - came from: from a pear, from a candle for a chandelier or a sconce. And got the letter C in the abbreviation, for example, from the Latin word "candela", translated as "candle". CA - "candle in the wind," and CF - "twisted candle."
For clarity we recommend a series of thematic videos.
Modern electric sources of artificial light are astonishingly diverse. For any type of lighting fixtures you can choose several varieties of bulbs in terms of price and energy efficiency. For example, for sconces or chandeliers, LED or LON "candle" or "candle in the wind" will do. For retro light fixtures, choose an Edison bulb or a modern LED "corn".