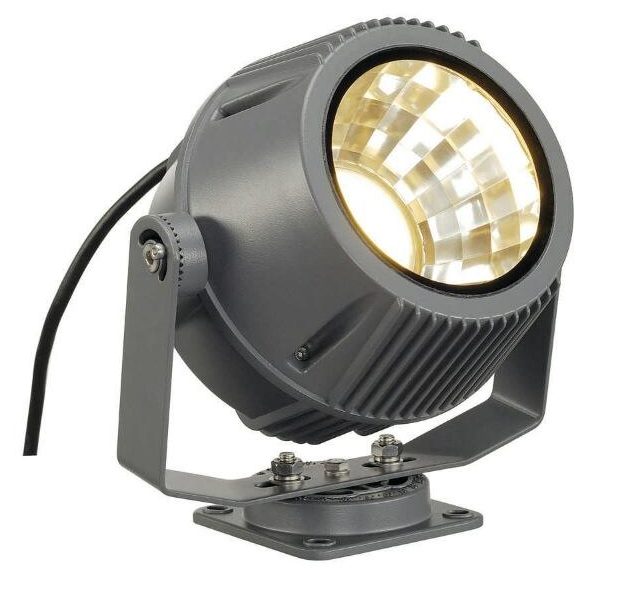
What is a spotlight
Among lighting devices, a separate niche occupy spotlights from the Latin projectus "directed or thrown forward" - a device that concentrates the light beams in a certain direction by reflecting a cone-shaped or parabolic reflector. The idea was first reflected in the drawings of Leonardo da Vinci, and in Russia it was put into practice by Ivan Petrovich Kulibin under Catherine the Great in the ninth century. He made an optical telegraph with a system of mirrors redistributing light from ordinary wax candles into a directional beam.
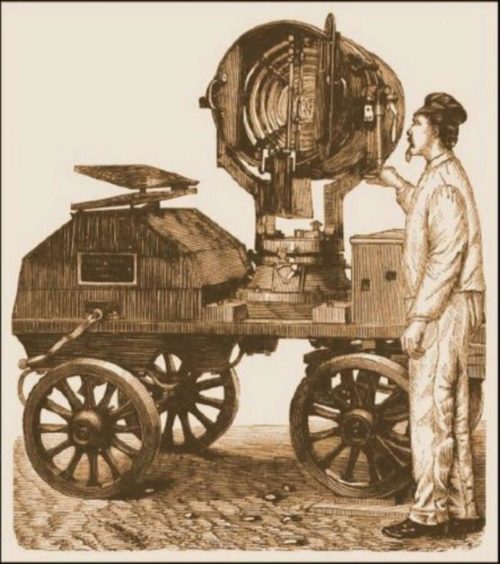
The invention was used as a semaphore in the Navy and in land communications, the scientist illuminated the dark passages of the Palace of Tsarskoye Selo. Later the topic was developed in a military direction with electric light sources, and the reflector scheme was used in almost all lighting devices where a concentrated beam of light was needed.
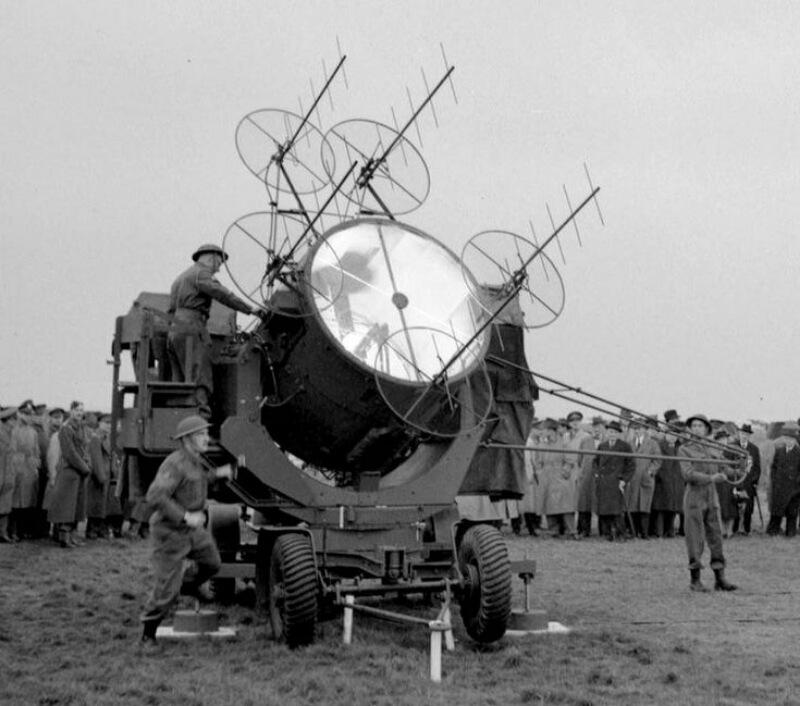

To increase the range it was necessary to increase the diameter of the parabolic reflector and some types of projectors reached the dimensions of 2 meters in diameter. Later on, focusing lenses were installed instead of protective glass. Though a part of useful spectrum of luminescence is lost in the lens, this solution allowed to save on reflecting surface area and to produce compact devices up to hand-held ones.
Spotlight characteristics
Based on the task set for the device, the manufacturers of lighting equipment produce products with certain properties that are not so much related to the design of the device, but directly to the light emitted by it, namely:
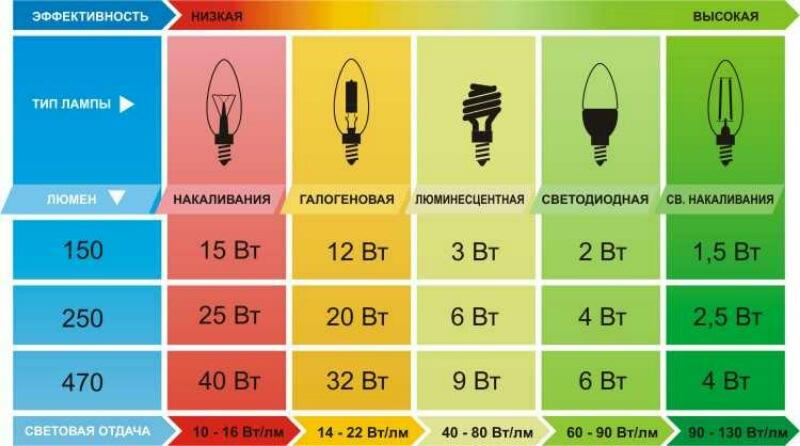
- power - is the power consumption of a light source, expressed in watts (W). The higher the power, the brighter and farther the lamp reaches. At the same time, different types of the same power have different energy efficiency - the ratio of energy consumption to light output;
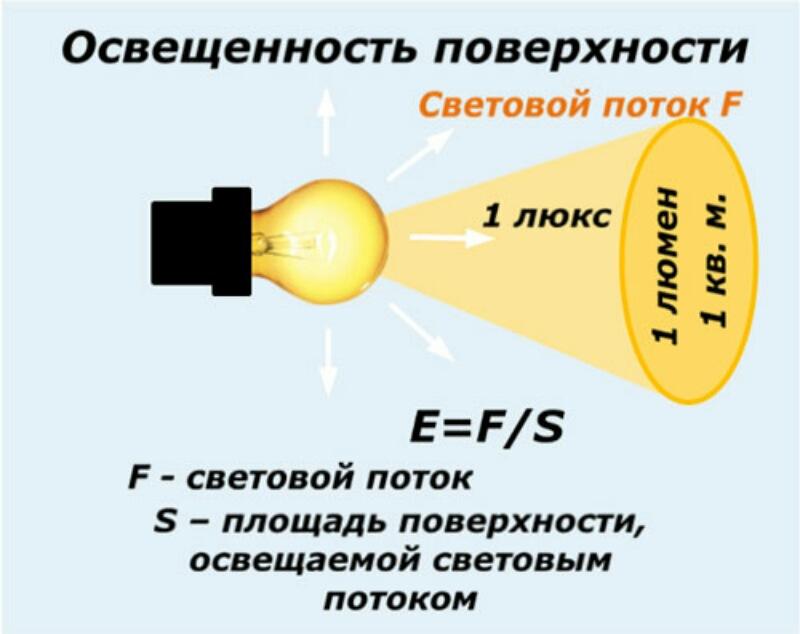
- luminous flux - is the main characteristic that determines the efficiency of a light source, expressed in lumens (Lm). However, the final efficiency of a projector, taking into account all optical losses, is measured in lux with a luxmeter;
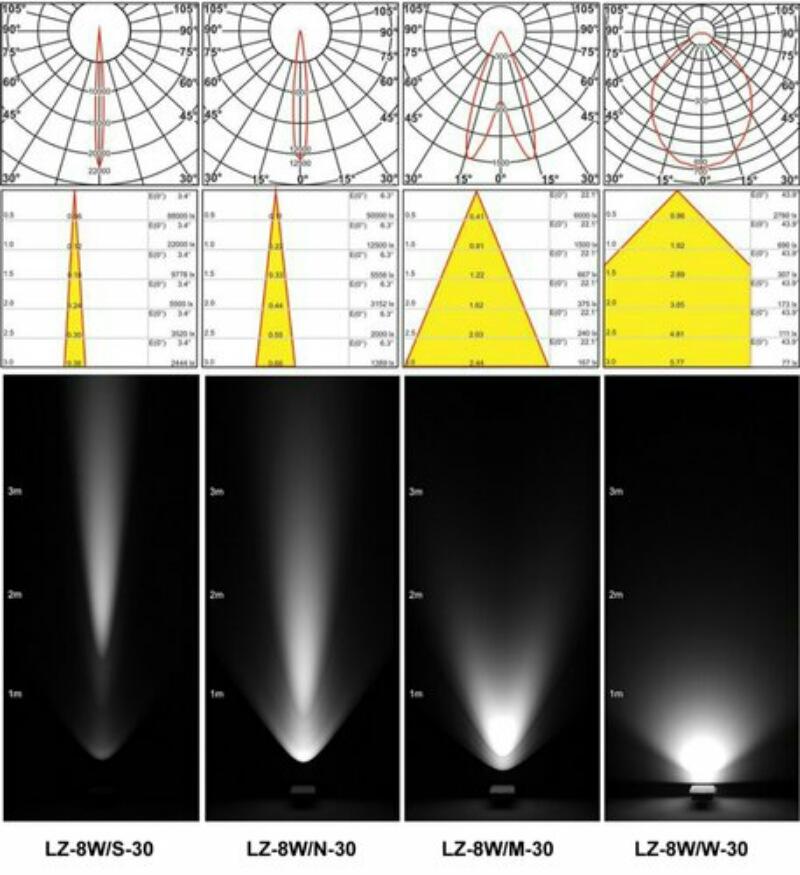
- Scattering angle - depending on the design and diameter of the reflector formed the angle of the divergence of the light cone from 6 to 160 °. The smaller the angle the farther the device will shine, but the side lighting will be minimal. And vice versa: the larger the angle, the greater the area covered by the light spot with a minimum range;
- light temperature - The hue of the illuminated object, measured in Kelvin (K). Varies from red to white. The temperature determines the color rendering index, a parameter that determines how naturally the color palette is perceived by the human eye. The best color rendering index lies in the neutral range of 3500-4500 K.
Warm light is weaker, but penetrates fog, snow, and rain better. In good visibility conditions, the cool shade covers a greater distance, although the colors and outlines of objects may blend into a single spot.
Depending on the intended operating conditions, spotlights have certain design features:
- Power source - most units are powered directly from 220 V mains, but some types of lamps require a ballast or driver. As a rule, these circuit elements are included in the design of the device initially or connected externally. There are also stand-alone spotlights powered by batteries, gasoline or diesel power generators;LED driver
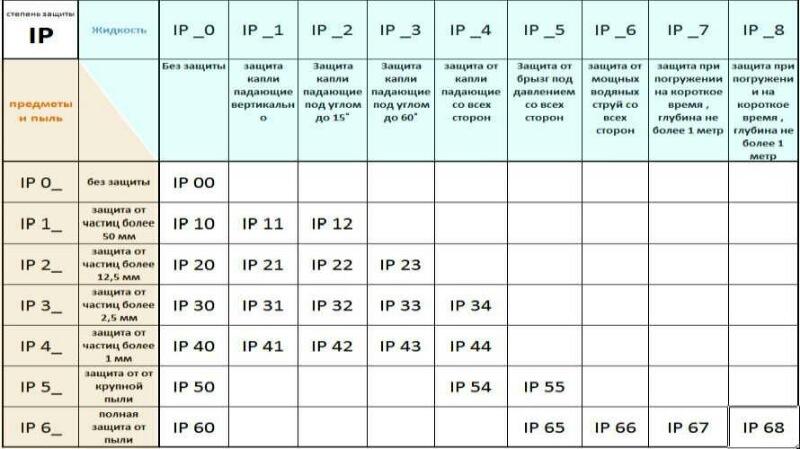
- protection level - A characteristic that determines the factors and environmental conditions under which the enclosure of the unit guarantees stable operation of the system. According to the international classification, IP is measured in numbers relative to the degree of protection against particulate matter and moisture.
Types of spotlights
The main design difference concerns the source of light. The first, relatively efficient electric flashlights were equipped with electric arc lamps of Edison or Ilyich with a filament of carbon, platinum, tungsten. Although the platinum filament demonstrated the greatest resource and light output due to economic inexpediency it was replaced by cheaper tungsten. Subsequently the evolution of lamps was directed towards increasing efficiency, service life, compactness and cheaper production.
Halogen
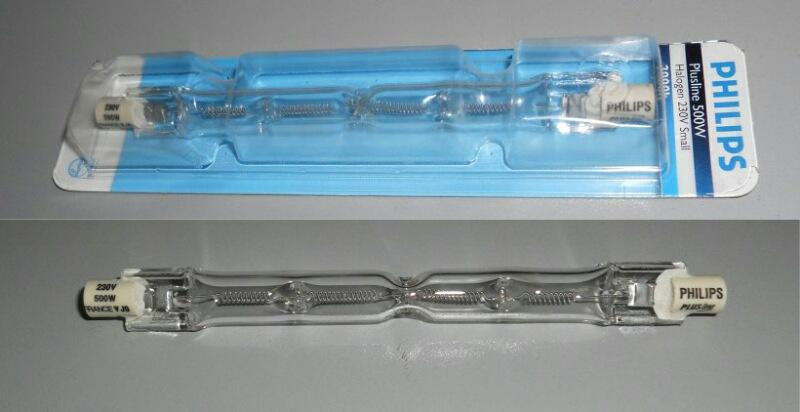
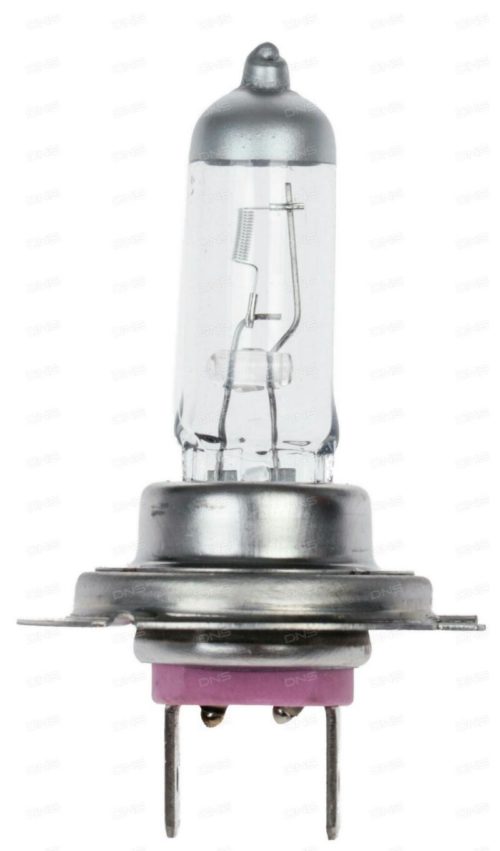
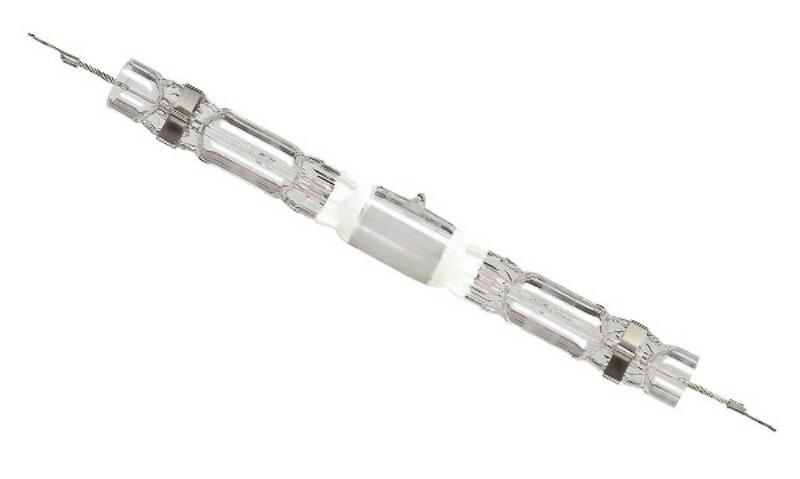
The first modification of incandescent lamps was a quartz glass bulb filled with inert gases and iodine halogens. In an inert environment, the filament does not burn out as intensely, which allowed for higher voltage and greater light output. For spotlights, the most common type is the linear halogen lamp with a double-sided R7s base
For round reflectors there are smaller lamps with pin-type G bases.
Energy efficiency halogen lamps is 22 lm/watt on average compared to 15 lm/watt for Ilich bulbs. Their service life is also increased by at least 1.5 times. A transformer is needed for power supply, but there are kinds designed for direct plugging into a 220V network.
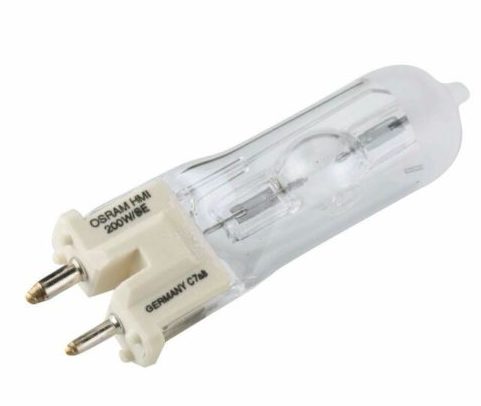
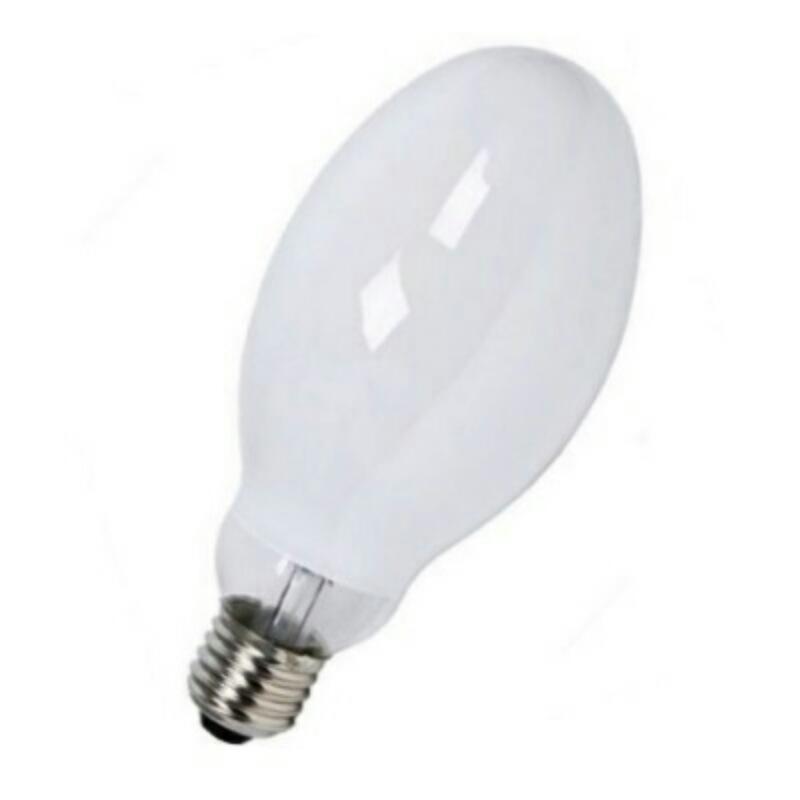
Metal halide .
These consist of a double glass bulb, the inner one containing under high pressure various metal halides - gases capable of glowing when activated by a discharge of electricity. There is no conductor or filament in the design. The most common lamp type has an E27 or E40 screw base, but studio, stage lighting sometimes uses single-sided and double-sided pin bases.
MGLs have high color rendering, a lifespan of up to 20,000 hours and energy efficiency of 85 Lm/W. To start the device requires a choke - a ballast, among other things, maintains the stability of operation during power supply fluctuations. The lamps do not need to be heated up and can be started up at -40°C, which makes them suitable for use in northern latitudes.
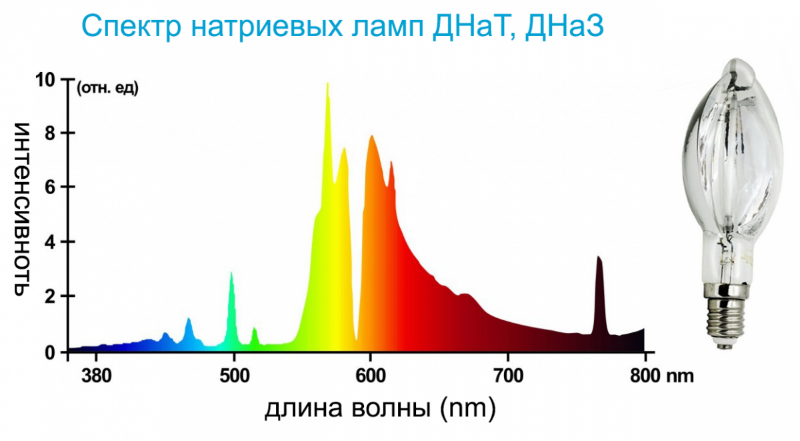
Sodium lamps (DNaT)
They do not differ much structurally from metal halide lamps. Sodium salts are added to the inner bulb which gives a strong stream of light energy in the yellow and red spectrum by evaporating. The high-pressure lamps lamps have an energy efficiency of about 130 Lm/Watt, and low-pressure lamps up to 180 Lm/Watt. The monochrome spectrum of luminescence distorts the color rendering, but is as close to the solar spectrum in the ranges necessary for photosynthesis of plants. It is these types of spotlights that are most often installed in greenhouses.
Standard types of lamps have a screw base, but there are varieties with a pin base.
To simulate daylight and improve color rendering, there are samples with painted white glass.
Salt vapors glow less intensely in freezing temperatures below 35°C. The devices are very sensitive to power fluctuations in the mains, so they need a choke for operation and ignition choke. Service life varies in the range of 13000-15000 hours, followed by a drawdown in the luminous flux.
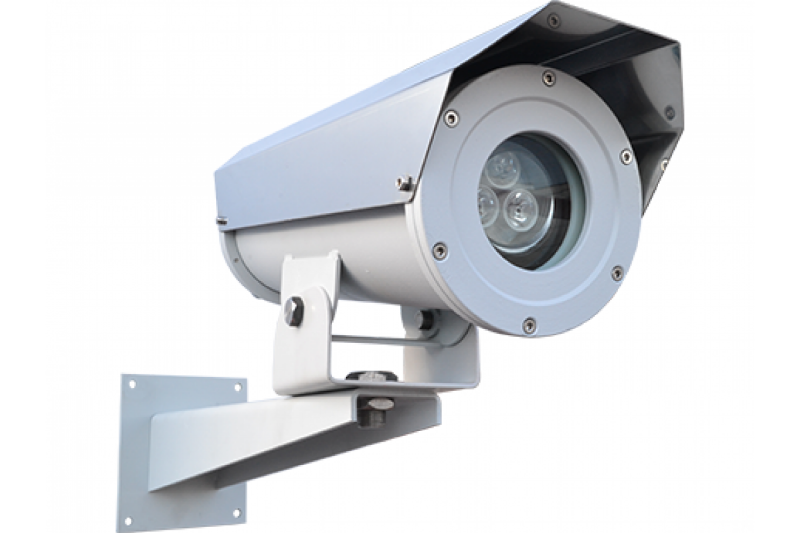
Infrared illuminators
Unlike other lighting devices, infrared lamps emit only the invisible to the human eye infrared range of 800 nanometers. In combination with video cameras designed to work in these ranges represent a covert nighttime surveillance system.
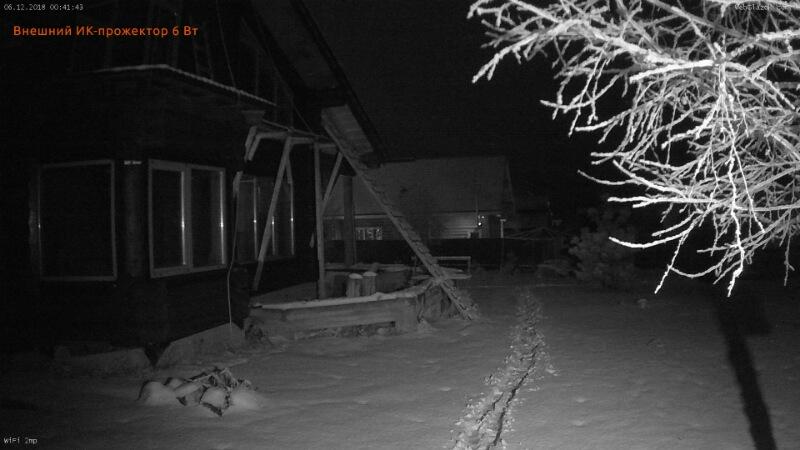

The camera picks up only the reflected rays from IR illuminators in black and white, and the rest of the space appears unlit. These units use gas-discharge or LED lamps with a preset glow spectrum are used as a light source for these devices.
For your information! There are rare anomalies of human vision in which the IR rays are partially visible.
LED
Widely used over the past 20 years because of their compactness, low cost and energy efficiency in the range from 70 to 130 Lm/W. There are two types of LED bulbs used for spotlights:
- COB - Crystals that are closely spaced and filled with phosphor. They produce a uniform flow of light, but are very hot and therefore require a massive heat sink or forced cooling.
- SMD - Matrices with a set of led elements of the same power.
Have more variation, but due to the space between the elements have a better heat dissipation. When connected in series, if one LED burns out, the entire board fails. В parallel The whole load falls on the remaining bulbs, which accelerates their wear and tear.
After frequent overheating LED elements, if they do not burn out, they give up to 30% slump. In this regard, manufacturers pay more attention to SMD matrices, which are not so demanding to heat dissipation. American Cree, Japanese Nichia or German Osram LEDs produce an average of 100 lm/W and have a service life of up to 50,000 hours.
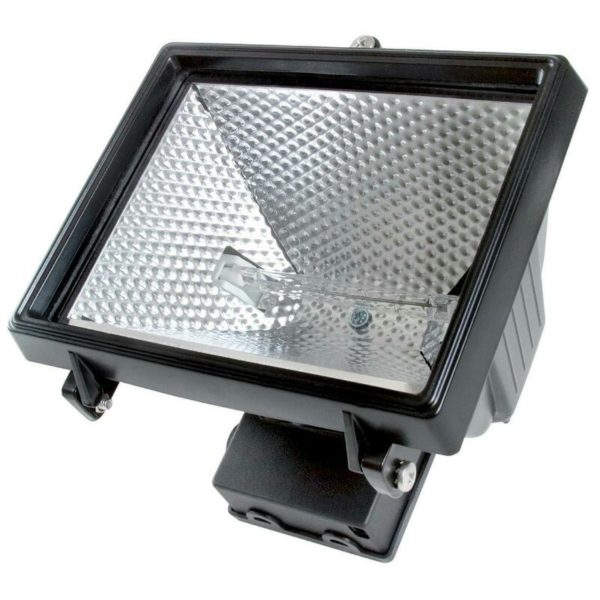
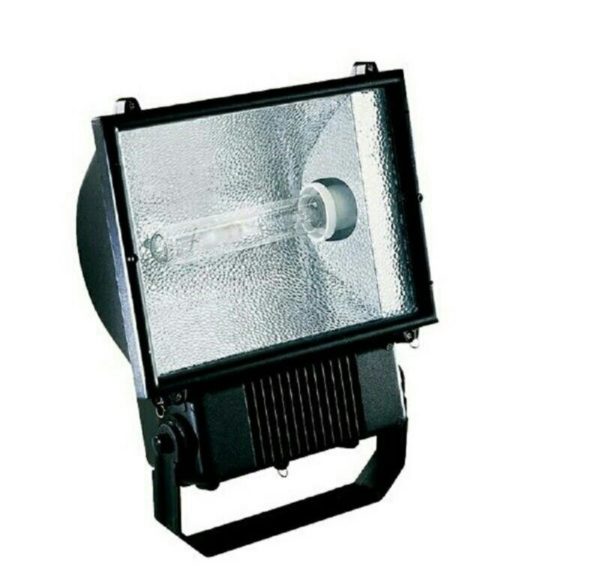
Spotlight design
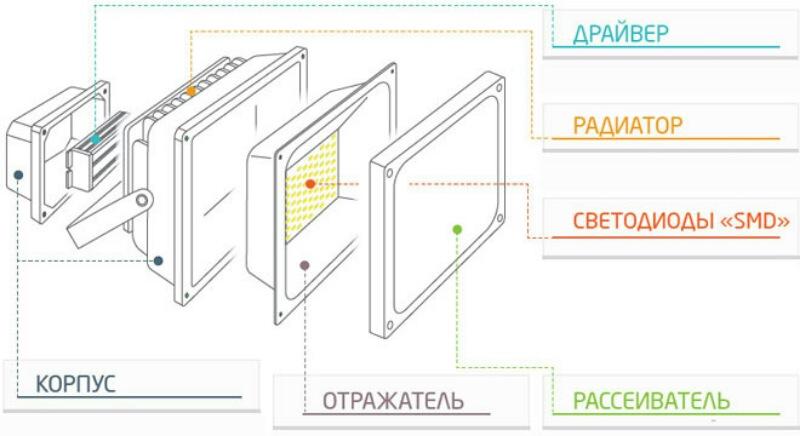
Traditionally, the design consists of the following elements:
- housing - The housing is made of plastic or metal. The best solution is if the entire enclosure is made of aluminum: lightweight, corrosion-resistant and with sufficient thermal conductivity. The rear part is equipped with a metal radiator;
- reflector - reflector made of shiny metal or foil-coated plastic that acts as a mirror to focus the beam;
- protective glass - Sometimes made of heat-resistant polycarbonate. In models with a wide angle of dispersion, it is corrugated for better distribution of the light spot. Some models have a focusing lens instead of glass;
- light source;
- power supply - represented by a transformer, driver or choke depending on the type of lamp. It may not be present if the device works directly from the 220 V mains or connected externally.
A separate niche is occupied by fully autonomous devices with a solar panel and a battery. Some models are equipped with light and motion sensors to automatically turn on at night or when a moving object enters the sensor's field of view.
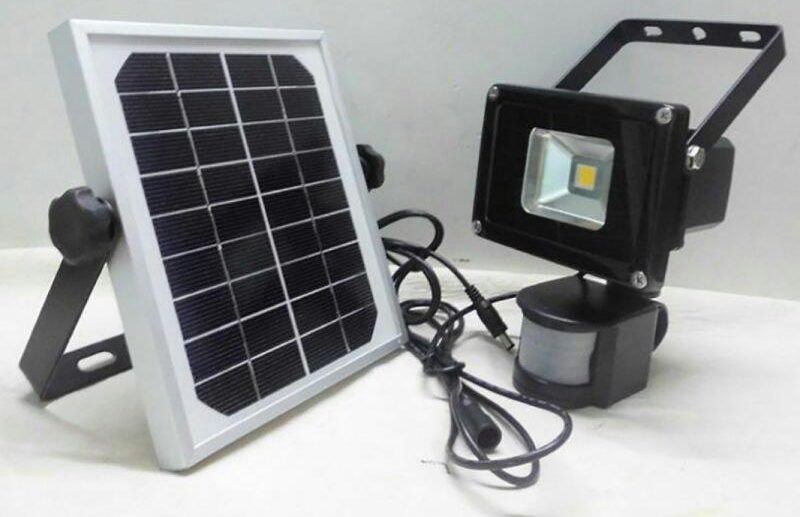

Depending on their purpose, the devices have several types of mounting:
- On the console.
- Bracket.
- Tripod.
- Suspension.
- Ground peg.
- Portable version.
- Rotary module.
Scope of application
Spotlights are ubiquitous in all areas of life, where you need to light large areas or long distances.