What is a LED - detailed description of characteristics and types
LEDs are present everywhere: in homes, cars, phones. They provide a bright backlighting screens of gadgets, produced cost-effective light sources. Now it is an indispensable source of light. Consider the device and technical characteristics of the main types of LEDs.
What is a LED
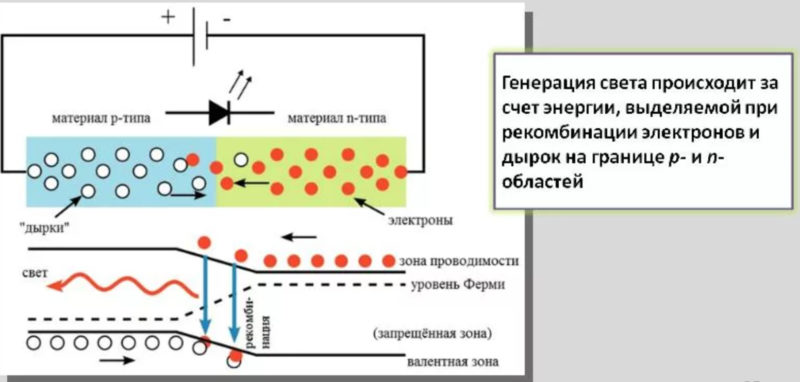
LED (from Light Emitting Diode, or LED) - a solid-state electrical source of artificial light, made of semiconductor materials of p- and n-conductivity. Using several techniques - mask sputtering, etching, epitaxial deposition, etc. - a p-n junction is produced.
In a p-type semiconductor material, the current carriers are "holes" - atoms of the semiconductor crystal, which are doped with special metals to create a lack of electrons. In n-materials, the carriers are the excess electrons in the crystal.
The "hole" is actually stationary. It has a positive charge equal to the charge of the electron. The electron, "jumping" from the outer orbit of one atom to the outer orbit of a neighboring atom, moves the "hole" in the opposite direction.
How it works or what glows in an LED
Electric current in the form of a countercurrent flow of electric charge carriers - "holes" - positive "particles" and electrons - negative ones can be induced by connecting a constant voltage of a certain magnitude and polarity to a p-n junction. When these fluxes meet in the p-n junction, they recombine or merge. A free electron with increased energy enters the "hole" and it disappears.
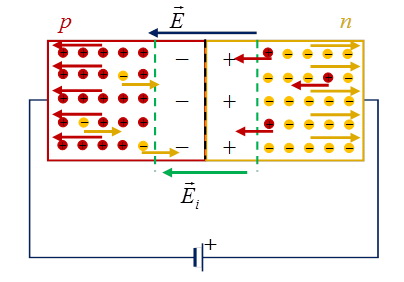
On the right is the n-semiconductor part of the crystal "enriched" with free electrons, on the left is the p-semiconductor part with positive "particles" - "holes".
Energy is released in the form of quanta of light. They are emitted, i.e. emitted from the end of the crystal. The flow of quanta hits the reflector. Its polished surface reflects the light in the desired direction. The desired directional pattern of the luminous flux is formed by the special configuration of the surface.
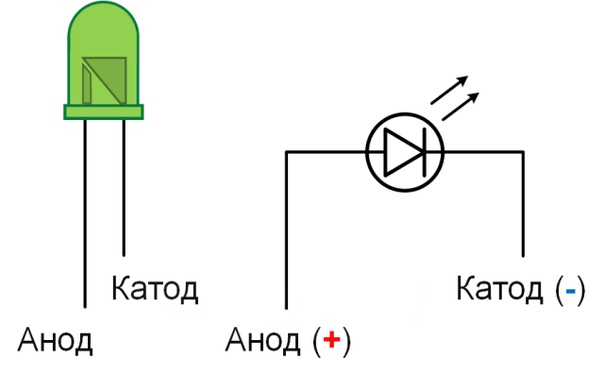
The voltage to energize the junction is applied "+" to the anode of the diode, and "-" to the cathode.
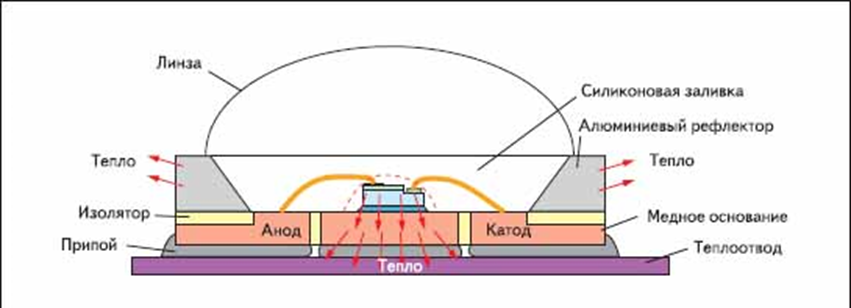
Design
The lilac color shows the heat sinking substrate. Gray trapezes are sections of a reflective reflector-reflector of a circular configuration of aluminum. In the center of blue - LED chip-crystal with connected gold or silver wires, soldered to the pins of the anode and cathode.
Types of LEDs
LEDs - a fairly "young" device. Their final classification has not yet been formed. Therefore, many well-known manufacturers use their own subdivision systems.
According to one of them, LEDs by purpose are grouped as follows:
- Indicator.
- Illuminating.
Indicator LEDs in their group are divided into the following types.
DIP diodes .
The abbreviation is derived from Dual In-line Package or "double in-line placement". The bodies are usually cylinders, but there are also parallelepipeds. On the lower end, the wire axial leads are parallel to the main axis of symmetry of the case. The cathode lead is shorter than the anode lead.
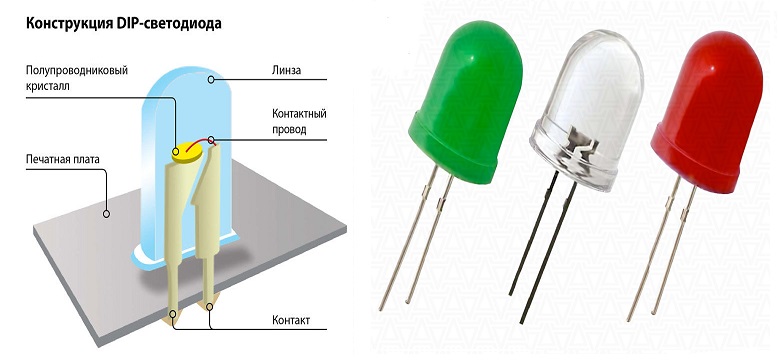
The division into types is by case diameter and the lens on the top end. Diameters range from 2-3 to 20 mm or more. The glow color is any color, there are several white shades.
One type is flashing in 2 colors and has 3 leads.
Straw Hat.
The literal translation is a straw hat or bryl. Applied to LEDs – The housing looks like a hat with a rounded top.
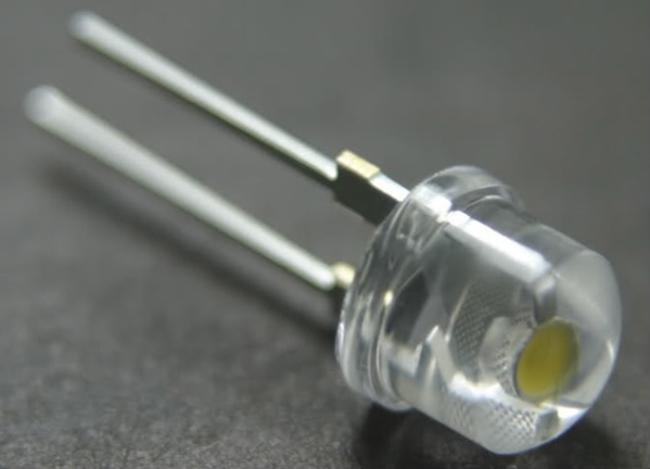

You can see the leads of different lengths, the short one is the cathode. You can also see the mounting height limiters. Under the lens is a crystal with a yellow phosphor.
Super Flux "Piranha"
Direct translation - super flux. Piranha - translated into Russian - piranha. The name LED got because of the features of the metal terminals in the form of narrow strips. To make it easier to insert it into the holes on the circuit board, the corners of the leads were cut off when stamping. This resulted in the sharp "teeth" of a predatory fish.
The "shoulders" - limiters that set the height of the case above the board - were stamped on the pins. This opened up the case for air cooling from below. Crystals for passive cooling were placed on the upper ends of the pins.
By placing 2 or 3 chips in the case, the light flux was increased. And the diode is in the super-bright group.

You can see the crystal "covered" by the lens and the tapered pins-formers of the mounting height.
SMD
Abbreviation of Surface Mounted Device, translated from English - surface mounted device. They look like rectangular plastic or ceramic housings. Terminals are at the bottom and on the side of the housing in the form of contact pads.
Most often - lighting, but at low power can be and indicator. Capacities range from mW (milliwatts) to W. Glow - any color or shade of white light.
Read also: Characteristics of SMD LEDs
OLED
In addition to solid-state LEDs based on semiconductor metals - silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, etc., there is a group of LEDs on the films of organic compounds. They are called organic or OLED-LEDs - Organic Light Emitting Diode.
They also, like semiconductor diodes, emit light, but not by a solid-state structure, but by thin films. So far, the main use is in the development of monochrome displays. The existing disadvantages of color OLED films - different in duration of the films of different colors of luminescence. At a minimum it is about 12-15 thousand hours.
Such LEDs after perfection will be widely used in cell phones, automobile and marine GPS-navigators, night sights and devices for night hunting and shooting, etc.
Video - overview: QLED, OLED and LCD (IPS) comparison.
Filament
In 2012-2013 there were unusual LEDs, which are called Filament. They are COB matrices in the form of long cylinders with diameter 2-3 and length 15-30 mm. On a glass or sapphire cylinder glued 28-30 blue crystals with a few splashes of red. They are connected in consecutive chains, and after checking their serviceability are filled with yellow phosphor.
This technology of making filament modules is called Chip-On-Glass or COG.
Prefabricated COG matrices are placed on the armature of conventional incandescent lamps, installed in the base and placed in a glass or plastic bulb. The bulb is filled with helium to cool the LEDs.
Power of the lamps is from 2-3 to 10-12 watts. The luminous flux corresponds to the luminous efficiency of conventional LEDs of 80-100 Lm/W.
As a result, the LED retrofit of the incandescent bulb was obtained. Often the lamp is incorrectly referred to as an LED incandescent bulb.
The term retrofit comes from the English retrofit - modernization or modification. These are new light sources in housings with traditional dimensions.


The pictures above show different wattages and manufacturers LED filament lamps. In a glass bulb with E27 base, filament COL modules are attached to the filament fixture.
PCB Star species
The abbreviation for this type of LED is derived from the English word combination Printed Circuit Board. Its translation is printed circuit board.

PCB Star diode board. The manufacturer is an American company CREE, Model XML diode. The yellow rectangle is the COB matrix of the high power diode.
The board is made of a metal that conducts heat well, such as aluminum. The configuration of the board is a 6-beam star. The COB LED matrix is factory mounted in the center of the star board. The board is painted black to increase the passive heat dissipation generated by the high-power operating light-emitting device.
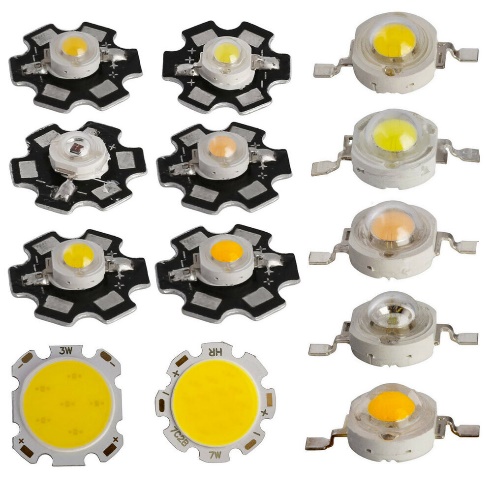

The 6 "stars" on the left are diodes of different power and shades of white light. The two at the bottom are more powerful elements with large circles of yellow phosphor. On the right is a column of 4 pieces. - diodes for planar mounting on the surface of the contact pads on the printed circuit board.
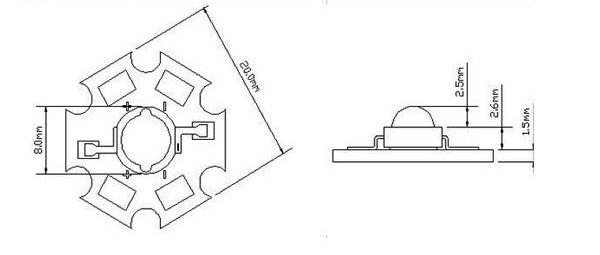
Dimensional drawing of a high-power planar LED on a star board. The construction height is 6.6 mm, the body diameter of the diode with planar pins is 8 mm, the size of the Star board is 22 mm.
COB LED matrix
If on a thermally conductive substrate of an artificial crystal of sapphire or silicon to glue dielectric glue a few dozen semiconductor crystals blue glow, connect their conductors in series-parallel groups and fill the top yellow phosphor, we get a LED module. This is COB matrix. The abbreviation is derived from the English word combination Chip-On-Board. It is translated as "crystals on a board".

COB matrices use coreless LED chip crystals without substrates. The placement is extremely dense. This technology is used to produce a significant portion of high-power LEDs, including hundreds of crystals. A good fan-blown heat sink, sometimes using heat pipes, can achieve 150-200 watts or more in a single package. The matrix provides directional flux with a 100-150 degree dispersion angle at 0.7 of maximum radiation.
Typical Classification
The types of LEDs can include:
- Single LEDs on a single high-power crystal (COB-matrix);
- pairs of LEDs in one package - indicator LEDs that flash alternately in two colors, such as red and yellow
- Triplets or triads of emitters with three primary colors - red, green and blue or RGB .Red, Green, Blue.
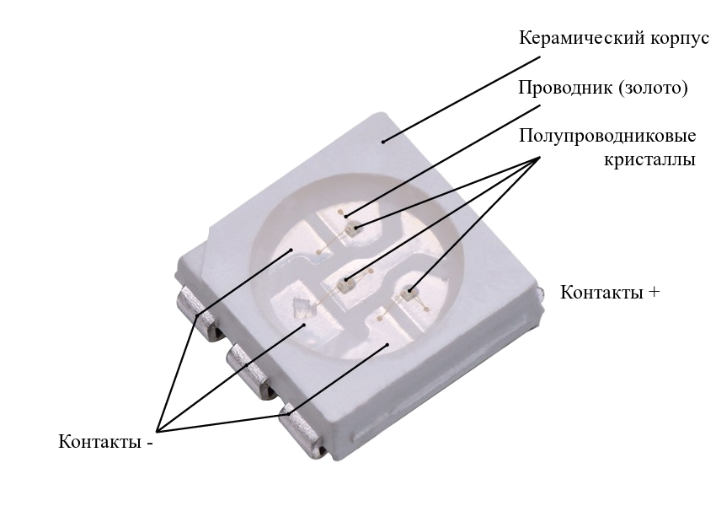
If a three-crystal LED has crystals of the same color we have a super-bright LED. With different colors of light crystals we have RGB triad, or multicolor controlled light-emitting device.
SMD - Abbreviation for Surface Mounted Device. Used for automation of placement and soldering of electronic components on printed circuit boards, including LEDs. Used in ribbons, strips, modules and conventional printed circuit boards.
The basic colors include a pair of colors YB - Yellow, yellow and Blue, blue. There are other combinations of colors that give a white color after mixing.
Powerful COB LEDs
The larger models have mounting holes in the corners of the housing. The smaller models are attached by soldering to a printed circuit board.
In addition to the usual characteristics of LEDs in high-power models, several additional parameters are added:
- power rating, W;
- chip size, mm;
- rated operating current of the crystal or matrix;
- Service life associated with standards L 70, L80, etc.
Low-power LEDs
By the value of power consumption are LEDs from 0.05 to 0.5 W, operating current - 20-60 mA (average power - 0.5-3 W, current 0.1-0.7 A, large - more than 3 W, current 1 A and more).
Structurally, low-power LEDs include several groups of LED light emitters:
- SMD conventional and super-bright LEDs;
- DIP-type diodes in cylindrical packages for mounting in board holes;
- in "piranha" packages - for mounting in holes.

The picture shows the LEDs from top to bottom:
- In DIP-type cylindrical packages - with flexible wire leads for soldering into board holes.
- In piranha type enclosures, aka Superflux, solder to holes.
- In the case with planar pins for mounting on the contact pads of single- and double-sided PCBs or in the "wells" of multilayer boards.
Features of LEDs
LEDs are described by a number of parameters. The most important ones are:
- Light intensity and energy efficiency - Lm and Lm/W;
- angle of divergence of luminous flux at 0.5 or 0.7 degrees, degrees - in conventional models from 120 to 140 degrees, the indicator models - from 15 to 45 degrees
- operating power, W - small - up to 0,5, medium - 0,5-3, large - more than 3;
- Operating current through the diode, mA or A;
- color or shade of white light, color temperatureKelvin, K - from 2000-2500 K - warm white and up to 6500-9500 K - cool white.
There are other characteristics, but they are used less frequently. For example, the volt-ampere characteristic, or VAR, of an LED is a curve of dependence of the current through the junction on the operating voltage applied to it. It is used in electrical calculations of the LED operating mode.
Dimensions .
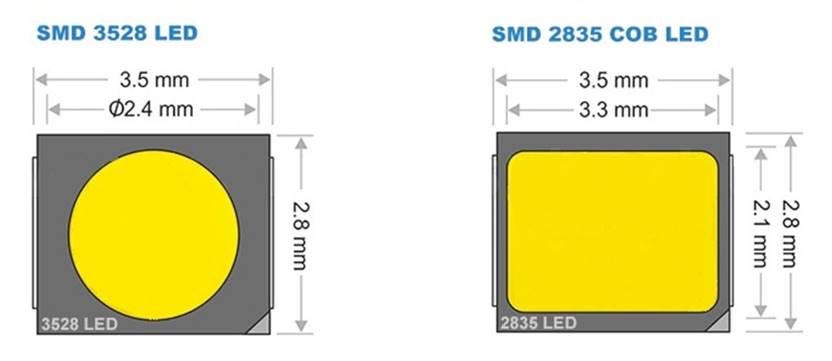
Dimensions of the LED are determined by the dimensions of its housing. For SMD housings - length, width, thickness. The first two values are embedded in the designation, for example, SMD2835, where two pairs of digits are 2.8 mm - width and 3.5 mm - length. The thickness of the body should be taken from the description or the passport of the diode.
For cylindrical DIP diodes the important features are the diameter of the housing and its height with the lens. Consider the length of the wire leads and the manufacturer's recommendations for bending them before mounting.
Wavelength
Such a characteristic of LEDs as wavelength is used very rarely. More often referred to the color of luminescence.
| Color shade | Wavelength, nm |
|---|---|
| Infrared (invisible) | 760-880 |
| red | 620-760 |
| orange | 585-620 |
| yellow | 575-585 |
| yellow-green | 555-575 |
| green | 510-555 |
| blue | 480-510 |
| blue | 450-480 |
| purple | 390-450 |
| Ultraviolet (invisible) | 10-390 |
The wavelength of a diode is measured in nanometers - nm. It is not always specified in the product data sheet.
Designation and color coding
Each manufacturer has its own labeling of LEDs. For example, in the designation of the LED - LED-WW-SMD5050 its alphabetic and numeric elements are deciphered:
- LED - LED;
- WW - Warm White - warm white 2700-3500 K;
- SMD - housing for surface mounting;
- 5050 - package dimensions in tenths of a millimeter - 5.0×5.0.
Abbreviation options for shades of white light:
- DW - Day White (4000-5000 K);
- W - White, pure white (6000-8000 K);
- CW or WC - Cool White - cool white (8000-10 000 K);
- WSC - White Super Cool - white super cool, color temperature 15 000 K with a characteristic bluish tint;
- NW - Neutral White - neutral white - 5000 K.
There are other designations of LEDs and colors, the system is not yet finally standardized, so manufacturers use different numerical values and names of shades of white light.
Graphical and alphabetic representation in the diagram
The anode, aka the plus of the LED in electrical diagrams is shown as a triangle. The cathode (minus) is shown with a cross dash.
LED voltage table
To ensure that the LED during operation all the features specified by its design and manufacturing technology, it needs to provide design power supply. For example, apply a voltage to its anode and cathode, which will be slightly higher than the direct voltage of p-n junction. The excess voltage should be "extinguished" with a series-connected resistor resistor. The resistor is called a current limiting resistor. It is used to prevent the current from exceeding the p-n junction.
The LED has two contact pins - anode and cathode, the cathode is shorter than the anode. If the length is the same, then determine with a thumbtack battery. If there is light, you have the anode.
Table. Direct voltage of the p-n junction of a colored light-emitting diode.
| Color of glow | Operating, direct voltage, V |
|---|---|
| white | 3,5 |
| red | 1,63–2,03 |
| orange | 2,03–2,1 |
| yellow | 2,1–2,18 |
| green | 1,9–4,0 |
| blue | 2,48–3,7 |
| purple | 2,76–4 |
| infrared | up to 1.9 |
| ultraviolet | 3,1–4,4 |
Read also: How to know how many volts a LED is
LED applications
The areas of application of LEDs are constantly expanding. Initially they were used as light indicators in the circuit of switching or operation of electronic equipment. For example, turning on a transmitter, switching to high or low power, etc. Could fix automatic switching on, for example, when a call signal appears or to attract attention. Flashing or single-color LEDs - red, yellow, green, blue - were used.
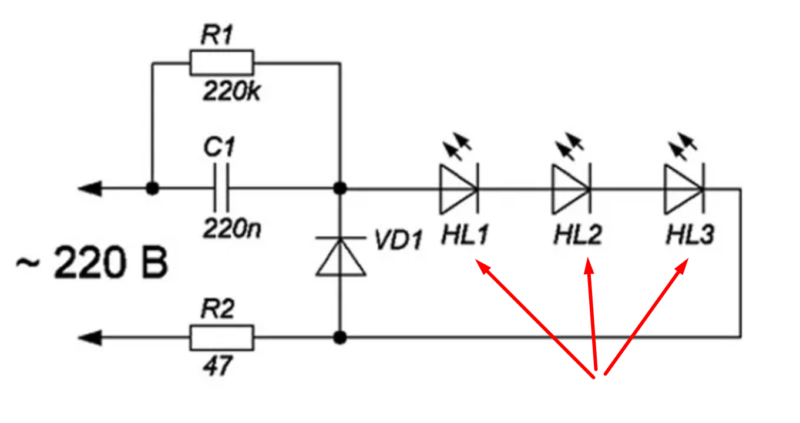
Small-sized super-bright DIP LEDs were connected in series-parallel chains and fed directly from a 220 V circuit. By placing these consecutive groups of diodes in a transparent PVC-tube and sealing them with a transparent sealant, we got "flexible neon" - a luminous "bundle". It can be laid on the edge of the pool, the curb of the path, decorate the roof of the house or a tree in the garden.

The advent of flexible multi-layer boards and SMD housings for surface mounting has led to the creation of flexible LED strips..
In the beginning it was a means of decorating the interior of the premises. Increasing the power of SMD-diodes and the density of their placement on the board allowed to start using LED strips first for auxiliary, and then the main lighting. Increasing the degree of dust and moisture protection of strips led to their use for decorative lighting, and then the main street lighting.
At the same time, LED lamps were being developed to replace incandescent lamps in lamps - wall lamps, chandeliers, table lamps. Retrofit lamps - full analogues of incandescent lamps and fluorescent tubes in shape, size of bulbs, power supply voltage appeared. The gradual replacement of incandescent lamps for LED retrofits began. At the same time, production of LEDs stopped - at first 100 W and more, then 75, 60, etc.
The development of high-power single LEDs, especially in the Emitter or PCB Star package, contributed to the appearance of flashlights with built-in battery. The brightness and duration of luminescence after one charge cycle was several times superior to previous models.
Excellent controllability of LEDs by electronic means - controllers and dimmers - Brightness controllers, allowed the use of powerful projectors in the light-dynamic illumination of streets and squares of cities and towns in any region of the country.

LED strips such as RGB, RGBW and RGBW made it possible not only to obtain a powerful stream of white light, but also to change its white color within a wide range from warm yellowish to bluish and cool blue.
The controllability of new light sources allows their wide use in light advertising - "crawl lines", light boards, information screens, etc. These bright colored and white light sources are used in facade advertising and on roofs - flat and volumetric letters and drawings, brand names, trademark images and much more.
And all these designs operate much longer than analogues on conventional lamps, almost no maintenance and consuming at the same time many times less electricity. The technical characteristics of LEDs and lighting equipment are constantly growing. The cost of LEDs is decreasing and applications are expanding.